
干旱区研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (1): 282-291.doi: 10.13866/j.azr.2022.01.27 cstr: 32277.14.AZR.20220127
收稿日期:2021-01-18
修回日期:2021-03-15
出版日期:2022-01-15
发布日期:2022-01-24
作者简介:王毓芳(1995-),女,硕士,研究方向为湿地生态水文过程. E-mail: 基金资助:
WANG Yufang( ),ZHAO Chengzhang(
),ZHAO Chengzhang( ),ZENG Hongxia,KANG Manping,ZHAO Tingting,TANG Yurui
),ZENG Hongxia,KANG Manping,ZHAO Tingting,TANG Yurui
Received:2021-01-18
Revised:2021-03-15
Published:2022-01-15
Online:2022-01-24
摘要:
湿地景观格局能够反映湿地类型的面积变化和空间分布特征,其时空演变有助于理解干扰因子与湿地生态过程之间的作用关系。选择疏勒河中游的库塘湿地、永久性河流湿地和内陆盐沼等5种湿地类型,采用景观格局分析法和主成分分析方法,研究了湿地类型面积、景观指数时空演变及其影响因素。结果表明:(1) 1987—2017年疏勒河中游湿地总面积减少了477.24 km2,其中库塘湿地、永久性河流湿地和内陆盐沼面积分别减少了50.99%、53.28%和35.78%,草本沼泽和沼泽化草甸面积增加了175.26%和21.89%。(2) 各湿地在景观水平和类型水平上,斑块密度和景观形状指数呈现波动增大趋势,湿地景观斑块趋向破碎化和零散分布。(3) 2017年人口、耕地较1987年分别增加了1.2倍和1.5倍,社会经济发展主要指标对湿地面积变化的解释度为68.89%,气候因子对其的解释度为22.09%。过去30 a人口增长、耕地扩张和水利工程建设导致了疏勒河中游湿地面积减少和景观破碎化。
王毓芳,赵成章,曾红霞,康满萍,赵婷婷,唐玉瑞. 疏勒河中游湿地景观时空演变及其影响因素[J]. 干旱区研究, 2022, 39(1): 282-291.
WANG Yufang,ZHAO Chengzhang,ZENG Hongxia,KANG Manping,ZHAO Tingting,TANG Yurui. Spatial-temporal evolution of wetland landscape patterns and its influencing factors in the middle reaches of the Shule River[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2022, 39(1): 282-291.
表1
疏勒河中游湿地景观类型及其解译标志"
| 湿地类 | 湿地型 | 景观特征 | 遥感影像特征 | 543波段 组合显示 | 野外实地图片 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 河流湿地 | 永久性河流湿地 | 有明显水面、河道以及水流痕迹 | 呈条带状分布,边界清晰,呈绿色、浅绿色,影纹均匀 | 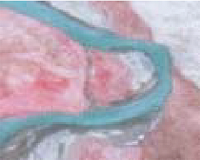 |  |
| 人工湿地 | 库塘湿地 | 水面规则明显,不杂乱,无其他景观交叉 | 形状规则,纹理均一,呈深蓝色 |  |  |
| 沼泽湿地 | 草本沼泽 | 分布于水体边缘,团状、块状簇拥集中,参杂裸露水面 | 形状不规则,呈黑红色或深红色,影纹不均、粗糙 | 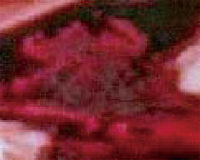 |  |
| 沼泽化草甸 | 分布于草本沼泽边缘,地势平坦、低洼处,景观较为均质,植被以苔草、嵩草为主 | 片状分布,边界不规则,呈浅红色,纹理比较均匀 | 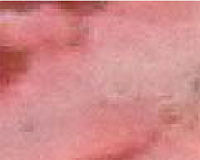 |  | |
| 内陆盐沼 | 集中连片,生长着芨芨草、赖草、芦苇,因植被盖度和类型不一,景观有明显的穿插现象 | 片状分布,有交叉纹路,呈淡红色或浅灰色 |  |  | |
| 主要以泌盐植物柽柳为优势种,地表长有高度较低的芦苇和赖草,面积较大 | 有点状、团簇状的红色斑点,质地粗糙 | 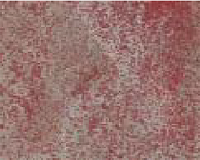 |  |
| [1] |
Zhao Wenzhi, Liu Bing, Zhang Zhihui. Water requirements of maize in the middle Heihe River Basin, China[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2009, 97(2): 215-223.
doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2009.09.011 |
| [2] | 徐晓龙, 王新军, 朱新萍, 等. 1996—2015年巴音布鲁克天鹅湖高寒湿地景观格局演变分析[J]. 自然资源学报, 2018, 33(11): 1897-1911. |
| [Xu Xiaolong, Wang Xinjun, Zhu Xinping, et al. Landscape pattern changes in alpine wetland of Bayanbulak Swan Lake during 1996-2015[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2018, 33(11): 1897-1911. ] | |
| [3] |
Cui Lu, Zhao Yonghua, Liu Jianchao, et al. Landscape ecological risk assessment in Qinling Mountain[J]. Geological Journal, 2018, 53: 342-351.
doi: 10.1002/gj.v53.S1 |
| [4] |
Gong Peng, Niu Zhengguo, Cheng Xiao, et al. China’s wetland change (1990-2000) determined by remote sensing[J]. Science China (Earth Sciences), 2010, 53(7): 1036-1042.
doi: 10.1007/s11430-010-4002-3 |
| [5] | 黄犁, 徐丽萍. 玛纳斯河流域绿洲时空演变及其景观格局变化[J]. 干旱区研究, 2019, 36(5): 1261-1269. |
| [Huang Li, Xu Liping. Spatiotemporal evolution of the oasis and change of landscape pattern in the Manas River Basin[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2019, 36(5): 1261-1269. ] | |
| [6] | 吴金华, 房世峰, 刘宝军, 等. 乌裕尔河—双阳河流域湿地景观格局演变及其驱动机制[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(13): 4279-4290. |
| [Wu Jinhua, Fang Shifeng, Liu Baojun, et al. Landscape pattern evolution of wetland and its driving mechanism in Wuyuer-Shuangyang River Basin[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(13): 4279-4290. ] | |
| [7] | 孙鸿超, 张正祥. 吉林省松花江流域景观格局脆弱性变化及其驱动力[J]. 干旱区研究, 2019, 36(4): 1005-1014. |
| [Sun Hongchao, Zhang Zhengxiang. Change of landscape pattern vulnerability in the Songhua River Basin in Jilin Province and its driving forces[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2019, 36(4): 1005-1014. ] | |
| [8] | 王晓峰, 延雨, 李月皓, 等. 银川市湿地景观演变及其驱动因素[J]. 干旱区研究, 2021, 38(3): 855-866. |
| [Wang Xiaofeng, Yan Yu, Li Yuehao, et al. Wetland landscape evolution and its driving factors in Yinchuan[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2021, 38(3): 855-866. ] | |
| [9] |
Chen Ang, Sui Xin, Wang Dongsheng, et al. Landscape and avifauna changes as an indicator of Yellow River Delta Wetland restoration[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2016, 86: 162-173.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2015.11.017 |
| [10] | 王效科, 欧阳志云, 苗鸿. 中国西北干旱地区湿地生态系统的形成、演变和保护对策[J]. 国土与自然资源研究, 2003, 25(4): 52-54. |
| [Wang Xiaoke, Ouyang Zhiyun, Miao Hong. Formation, evalution and protection of wetland ecosystems in arid region, Northwestern China[J]. Territory and Natural Resources Study, 2003, 25(4): 52-54. ] | |
| [11] | 姚鑫, 杨桂山, 万荣荣, 等. 水位变化对河流、湖泊湿地植被的影响[J]. 湖泊科学, 2014, 26(6): 813-821. |
| [Yao Xin, Yang Guishan, Wan Rongrong, et al. Impact of water level change on wetland vegetation of rivers and lakes[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2014, 26(6): 813-821. ] | |
| [12] | 章光新, 武瑶, 吴燕锋, 等. 湿地生态水文学研究综述[J]. 水科学进展, 2018, 29(5): 737-749. |
| [Zhang Guangxin, Wu Yao, Wu Yanfeng, et al. A review of research on wetland ecohydrology[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2018, 29(5): 737-749. ] | |
| [13] |
Liu Guilin, Zhang Luocheng, Zhang Qian, et al. Spatio-temporal dynamics of wetland landscape patterns based on remote sensing in Yellow River Delta, China[J]. Wetlands, 2014, 34(4): 787-801.
doi: 10.1007/s13157-014-0542-1 |
| [14] |
Zhang Yujuan, Qu Jianguang, Li Dan. Evolution and prediction of coastal wetland landscape pattern: An exploratory study[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2020, 106(Suppl.): 553-556.
doi: 10.2112/SI106-125.1 |
| [15] | 王根绪, 李元寿, 王一博, 等. 近40 a来青藏高原典型高寒湿地系统的动态变化[J]. 地理科学, 2007, 62(5): 481-491. |
| [Wang Genxu, Li Yuanshou, Wang Yibo, et al. Typical alpine wetland system changes on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in recent 40 years[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2007, 62(5): 481-491. ] | |
| [16] | 赵锐锋, 姜朋辉, 赵海莉, 等. 黑河中游湿地景观破碎化过程及其驱动力分析[J]. 生态学报, 2013, 33(14): 4436-4449. |
| [Zhao Ruifeng, Jiang Penghui, Zhao Haili, et al. Fragmentation process of wetlands landscape in the middle reaches of the Heihe River and its driving forces analysis[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(14): 4436-4449. ] | |
| [17] | 曾光, 高会军, 朱刚. 塔里木河三源流区湿地演化特征遥感分析[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2014, 28(3): 68-73. |
| [Zeng Guang, Gao Huijun, Zhu Gang. Wetland evolution process of the three headwaters in the upper reaches of the Tarim River watershed based on RS[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2014, 28(3): 68-73. ] | |
| [18] | 周亚军, 刘廷玺, 段利民, 等. 锡林河流域上游河谷湿地景观格局演变及其驱动力[J]. 干旱区研究, 2020, 37(3): 580-590. |
| [Zhou Yajun, Liu Tingxi, Duan Limin, et al. Driving force analysis and landscape pattern evolution in the upstream valley of Xilin River Basin[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2020, 37(3): 580-590. ] | |
| [19] | 岳东霞, 陈冠光, 朱敏翔, 等. 近20 a疏勒河流域生态承载力和生态需水研究[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(14): 5178-5187. |
| [Yue Dongxia, Chen Guanguang, Zhu Minxiang, et al. Biocapacity and ecological water demand in Shule River Basin over the past 20 Years[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(14): 5178-5187. ] | |
| [20] | 岳东霞, 苗俊霞, 朱敏翔, 等. 疏勒河流域陆地水储量与植被指数的时空耦合关系[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(14): 5268-5278. |
| [Yue Dongxia, Miao Junxia, Zhu Minxiang, et al. Spatio-temporal coupling between terrestrial water storage and Vegetation Index in Shule River Basin[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(14): 5268-5278. ] | |
| [21] | 潘竟虎, 刘晓. 疏勒河流域景观生态风险评价与生态安全格局优化构建[J]. 生态学杂志, 2016, 35(3): 791-799. |
| [Pan Jinghu, Liu Xiao. Landscape ecological risk assessment and landscape security pattern optimization in Shule River Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2016, 35(3): 791-799. ] | |
| [22] | Da Fuwen, Chen Xingpeng, Qi Jinghui. Spatiotemporal characteristic of land use/land cover changes in the middle and lower reaches of Shule River Basin based on an intensity analysis[J]. Sustainbility, 2019, 11(5): 1-19. |
| [23] | 章予舒, 王立新, 张红旗, 等. 疏勒河流域土地利用变化驱动因素分析——以安西县为例[J]. 地理科学进展, 2003, 22(3): 170-178. |
| [Zhang Yushu, Wang Lixin, Zhang Hongqi, et al. An analysis on land use changes and their driving factors in Shule River: An example from Anxi County[J]. Progress in Geography, 2003, 22(3): 170-178. ] | |
| [24] | 杜际增, 王根绪, 杨燕, 等. 长江黄河源区湿地分布的时空变化及成因[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(18): 6173-6182. |
| [Du Jizeng, Wang Genxu, Yang Yan, et al. Temporal and spatial variation of the distributive patterns and driving force analysis in the Yangtze River and Yellow River source regions wetland[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(18): 6173-6182. ] | |
| [25] | 常跟应, 张文侠. 基于生态文明的疏勒河流域大规模移民反思[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 50(3): 405-409. |
| [Chang Genying, Zhang Wenxia. Ecological civilization-based rethinking of large-scale immigration and land development along Shule River[J]. Journal of Landzhou University (Natural Sciences), 2014, 50(3): 405-409. ] | |
| [26] | 章光新, 武瑶, 吴燕锋, 等. 湿地生态水文学研究综述[J]. 水科学进展, 2018, 29(5): 737-749. |
| [Zhang Guangxin, Wu Yao, Wu Yanfeng, et al. A review of research on wetland ecohydrology[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2018, 29(5): 737-749. ] | |
| [27] | 李山羊, 郭华明, 黄诗峰, 等. 1973—2014年河套平原湿地变化研究[J]. 资源科学, 2016, 38(1): 19-29. |
| [Li Shanyang, Guo Huaming, Huang Shifeng, et al. Variation in Hetao Basin wetlands from 1973 to 2014[J]. Resources Science, 2016, 38(1): 19-29. ] | |
| [28] | 刘彩红, 王翀, 曾平, 等. 丹江口水库水源地生态节地型人工湿地设计——以内乡县温家堰河内源治理与湿地修复工程为例[J]. 农业开发与装备, 2020, 25(3): 77-78. |
| [Liu Caihong, Wang Chong, Zeng Ping, et al. Design of ecological land saving constructed wetland in Danjiangkou Reservoir: Taking wenjiayan river source control and wetland restoration project in Neixiang County as an example[J]. Agricultural Development Equipments, 2020, 25(3): 77-78. ] | |
| [29] | 吕金霞, 蒋卫国, 王文杰, 等. 近30 a来京津冀地区湿地景观变化及其驱动因素[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(12): 4492-4503. |
| [Lyu Jinxia, Jiang Weiguo, Wang Wenjie, et al. Wetland landscape pattern change and its driving forces in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in recent 30 years[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(12): 4492-4503. ] | |
| [30] | 张敏, 宫兆宁, 赵文吉, 等. 近30 a来白洋淀湿地景观格局变化及其驱动机制[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(15): 4780-4791. |
| [Zhang Min, Gong Zhaoning, Zhao Wenji, et al. Landscape pattern change and the driving forces in Baiyangdian wetland from 1984 to 2014[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(15): 4780-4791. ] | |
| [31] | 赵锐锋, 姜朋辉, 赵海莉, 等. 土地利用/覆被变化对张掖黑河湿地国家级自然保护区景观破碎化的影响[J]. 自然资源学报, 2013, 28(4): 583-595. |
| [Zhao Ruifeng, Jiang Penghui, Zhao Haili, et al. Effect of land use/cover change on landscape fragmentation of Zhangye Heihe National Wetland Nature Reserve[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2013, 28(4): 583-595. ] | |
| [32] |
Yu Haiyang, Zhang Fei, Kung Hsiang Te, et al. Analysis of land cover and landscape change patterns in Ebinur Lake Wetland National Nature Reserve, China from 1972 to 2013[J]. Wetlands Ecology and Management, 2017, 25(5): 619-637.
doi: 10.1007/s11273-017-9541-3 |
| [33] | 刘吉平, 李艾玉, 田学智, 等. 三江平原孤立湿地的形成及主要类型[J]. 湿地科学, 2014, 12(2): 141-147. |
| [Liu Jiping, Li Aiyu, Tian Xuezhi, et al. Formation and main types of isolated wetlands in Sanjiang Plain[J]. Wetland Science, 2014, 12(2): 141-147. ] | |
| [34] |
张金茜, 巩杰, 柳冬青. 地理探测器方法下甘肃白龙江流域景观破碎化与驱动因子分析[J]. 地理科学, 2018, 38(8): 1370-1378.
doi: 10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2018.08.020 |
|
[Zhang Jinxi, Gong Jie, Liu Dongqing. Dynamics and driving factors of landscape fragmentation based on Geo Detector in the Bailongjiang Watershed of Gansu Province[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2018, 38(8): 1370-1378. ]
doi: 10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2018.08.020 |
| [1] | 张群慧, 常亮, 顾小凡, 王倩, 马卯楠, 李小等, 段瑞, 犹香智. 1979—2020年柴达木盆地人体舒适度指数时空变化及趋势分析[J]. 干旱区研究, 2024, 41(8): 1300-1308. |
| [2] | 张宏伟, 别强, 石莹, 苏晓杰, 李欣璋. 黄河流域上游植被覆盖变化特征及其影响因素[J]. 干旱区研究, 2024, 41(8): 1385-1394. |
| [3] | 胡广录, 刘鹏, 李嘉楠, 陶虎, 周成乾. 黑河中游绿洲边缘三种景观类型土壤水分动态特征及影响因素[J]. 干旱区研究, 2024, 41(4): 550-565. |
| [4] | 朵海瑞, 傲云巴特尔, 吾健, 罗洪巍, 同德兴, 孔繁燕, 杨芳, 魏婷婷. 柴达木盆地可鲁克湖-托素湖自然保护区鸟类多样性[J]. 干旱区研究, 2024, 41(3): 521-526. |
| [5] | 孙玮婕, 乔斌, 于红妍, 赵彤, 陈奇. 基于活力-组织力-恢复力的黑河源区高寒湿地景观生态健康评估[J]. 干旱区研究, 2024, 41(2): 301-313. |
| [6] | 聂汉林, 樊良新, 郭琎, 张梦可, 王志君. 县域尺度下关中地区农作物水足迹时空特征及影响因素[J]. 干旱区研究, 2024, 41(2): 339-352. |
| [7] | 王昱, 李能安, 雒天峰, 张英, 袁兴鹏, 田苗, 信雅玲, 胡飞燕. 梨园河流域景观格局对地表水质的影响[J]. 干旱区研究, 2024, 41(11): 1831-1841. |
| [8] | 陆莹, 张敏, 王彦阁. 内蒙古黄河流域生态保护恢复优先区识别[J]. 干旱区研究, 2024, 41(11): 1946-1955. |
| [9] | 朱从祯,赵天良,孟露,杨兴华,何清,买买提艾力·买买提依明. 塔里木盆地浮尘滞空天气客观分型[J]. 干旱区研究, 2023, 40(9): 1391-1403. |
| [10] | 刘军彦,王世杰. 基于ICESat-2卫星测高数据的呼伦湖水位变化监测[J]. 干旱区研究, 2023, 40(9): 1438-1445. |
| [11] | 海龙, 周梅, 张嘉開, 洪光宇, 李凤滋, 费菲. 毛乌素沙地不同林龄杨柴灌木林土壤呼吸及其影响因素[J]. 干旱区研究, 2023, 40(7): 1107-1116. |
| [12] | 张泽宇, 吴晓静, 梁一鹏, 张晓霞, 查同刚. 乌拉山废弃矿山生态恢复的近自然植被空间配置模式[J]. 干旱区研究, 2023, 40(7): 1164-1171. |
| [13] | 齐润泽, 潘竟虎. 河湟地区生态脆弱性时空演变及影响因素研究[J]. 干旱区研究, 2023, 40(6): 1002-1013. |
| [14] | 邹易, 蒙吉军. 干旱区绿洲-城镇-荒漠景观演变及生态环境效应[J]. 干旱区研究, 2023, 40(6): 988-1001. |
| [15] | 马晓蕾,乔雅琦,王婕,焦士兴,张曼. 陕西省水生态足迹深度与广度时空格局及影响因素[J]. 干旱区研究, 2023, 40(3): 469-480. |
|
||