
干旱区研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (6): 1771-1781.doi: 10.13866/j.azr.2021.06.29 cstr: 32277.14.AZR.20210629
收稿日期:2021-02-09
修回日期:2021-04-02
出版日期:2021-11-15
发布日期:2021-11-29
作者简介:曾红霞(1996-),女,硕士研究生,主要从事湿地生态学研究. E-mail: 基金资助:
ZENG Hongxia( ),ZHAO Chengzhang(
),ZHAO Chengzhang( ),WANG Yufang,LI Xiaoya,ZHAO Tingting,TANG Yurui
),WANG Yufang,LI Xiaoya,ZHAO Tingting,TANG Yurui
Received:2021-02-09
Revised:2021-04-02
Published:2021-11-15
Online:2021-11-29
摘要:
高寒湿地是重要的水源涵养和生物多样性聚集地,研究其湿地景观格局演变及其影响因素有助于认识湿地生态系统的独特功能、演变规律以及环境影响机制。本研究基于1989—2019年的6期Landsat遥感影像数据,结合GIS技术、景观格局指数以及相关性分析等研究方法,分析了盐池湾高寒湿地景观格局时空演变特征及其影响因素。结果表明:(1) 1989—2019年盐池湾湿地总面积呈增加趋势,沼泽化草甸、永久性河流和内陆盐沼分别增加31.02%、17.53%和3.77%,草本沼泽和裸斑分别减少54.28%和9.5%。(2) 类型水平上,1989—2019年永久性河流和沼泽化草甸的破碎化降低,其余各类型湿地的破碎化增加;景观水平上,湿地景观形状趋于简单化,湿地破碎化程度增加,蔓延度和香浓多样性指数减少,湿地景观分布向均衡方向发展。(3) 气温和降水与湿地面积、景观格局指数之间存在差异化的相关关系。气候变化是导致盐池湾高寒湿地面积变化和景观格局演变的关键因素。研究高寒湿地景观格局时间序列动态演变特征,对于理解湿地的生态功能和生态过程具有重要的理论意义,对湿地可持续发展和景观规划管理具有实践意义。
曾红霞,赵成章,王毓芳,李晓雅,赵婷婷,唐玉瑞. 盐池湾高寒湿地景观格局演变及其影响因素[J]. 干旱区研究, 2021, 38(6): 1771-1781.
ZENG Hongxia,ZHAO Chengzhang,WANG Yufang,LI Xiaoya,ZHAO Tingting,TANG Yurui. Landscape pattern evolution and its influencing factors of alpine wetland in Yanchi Bay[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2021, 38(6): 1771-1781.
表1
盐池湾高寒湿地解译标志"
| 湿地类 | 湿地型 | 景观特征 | 影像特征 | 543波段组合显示 | 实地图片 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 沼泽湿地 | 草本沼泽 | 水生和沼生的草本植物组成优势群落的淡水沼泽,主要生长杉叶藻、中间型荸荠和海韭菜 | 呈片状分布,形状不规则,呈黑红色,影纹不均、粗糙 |  |  |
| 内陆盐沼 | 生长碱地风毛菊、芨芨草、赖草等盐生植被的沼泽,以苏打、氯化物和硫酸盐为主的盐土 | 呈片状杂乱分布,形状不规则,呈粉红色、青色,影纹粗糙伴有红黑点 | 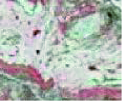 |  | |
| 沼泽化草甸 | 地势低洼、排水不畅、土壤过分潮湿、通透性不良等环境条件下发育,有早熟禾、苔草和嵩草等植物 | 呈片状、大块分布,形状不规则,呈红色,影纹不均 |  |  | |
| 裸斑 | 受强烈的蒸发作用,盐分在地表集聚,无生长植被,呈白色 | 边界清晰,形状规则,呈白色,影纹不均 |  |  | |
| 河流湿地 | 永久性河流湿地 | 有明显泥沙淤积、河道以及水流痕迹 | 常呈条带状分布,边界清晰,呈绿色、浅绿色,影纹较均匀 | 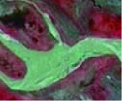 |  |
表2
景观格局指数计算公式及生态学意义"
| 景观指数 | 计算公式 | 生态学意义 |
|---|---|---|
| 斑块面积 | | 其大小反映了物种、能量和养分等信息的差异,值越大表示供给生物所需的物质和能量越多。式中:ai为斑块i的面积。 |
| 斑块数量 | NP=n | 反映了景观的空间格局,其值的大小与景观破碎度呈正相关,NP越大,景观破碎化程度越高。式中:n为某一斑块类型的斑块总个数。 |
| 最大斑块指数 | | 对于景观优势类型等的确定有重要作用,其数值越大,对景观总体的影响越大,优势度也越高,反之亦然。式中:分子为景观中最大斑块的面积;A为斑块总面积。 |
| 斑块密度 | | 反应景观的破碎化程度,值越大说明景观的破碎化程度越大。式中:N为景观中所有的斑块总数,A为总面积。 |
| 形状指数 | | LSI值越小,表明景观的形状越规整;LSI值越大,表明景观的形状趋于复杂。式中:A为总面积,E为景观中所有斑块边界总长度,0.25为正方形校正系数。 |
| 蔓延度指数 | | 其值越高,表明整体景观具有良好的连接性;其值越低,说明景观中连通性不好,破碎化程度较高。式中:m为景观中斑块总数;Pij为斑块类型i与j相邻的概率。 |
| 香浓多样性指数 | | 其值为0时,说明只有一个斑块组成了整个景观,随着SHDI增大,表明景观中不稳定信息在增多,破碎化程度在增大。式中:Pi为景观类型i的斑块占景观所有斑块的比例。 |
表3
1989—2019年湿地转移矩阵变化"
| 时段 | 景观类型 | 草本沼泽 | 裸斑 | 永久性河流湿地 | 沼泽化草甸 | 内陆盐沼 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1989—2007年 | 草本沼泽 | 6.00 | 2.07 | 2.93 | 9.06 | 7.55 |
| 裸斑 | 1.08 | 3.52 | 7.89 | 0.70 | 3.37 | |
| 永久性河流湿地 | 0.84 | 0.91 | 15.31 | 1.24 | 10.75 | |
| 沼泽化草甸 | 2.72 | 0.68 | 1.13 | 50.38 | 11.44 | |
| 内陆盐沼 | 1.15 | 0.95 | 3.73 | 7.44 | 71.31 | |
| 2007—2019年 | 草本沼泽 | 9.27 | 3.48 | 3.82 | 6.04 | 6.51 |
| 裸斑 | 1.15 | 7.70 | 4.70 | 0.70 | 3.30 | |
| 永久性河流湿地 | 1.44 | 3.26 | 11.08 | 0.76 | 2.38 | |
| 沼泽化草甸 | 10.93 | 1.14 | 3.10 | 48.63 | 13.49 | |
| 内陆盐沼 | 5.06 | 4.21 | 12.68 | 10.13 | 53.43 |
| [1] |
Guo M, Li J, Sheng C, et al. A review of wetland remote sensing[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(4):777.
doi: 10.3390/s17040777 |
| [2] |
Li Z, Jiang W, Wang W, et al. Ecological risk assessment of the wetlands in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2020, 117:106677.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106677 |
| [3] | 潘竟虎, 刘晓. 疏勒河流域景观生态风险评价与生态安全格局优化构建[J]. 生态学杂志, 2016, 35(3):791-799. |
| [ Pan Jinghu, Liu Xiao. Landscape ecological risk assessment and ecological security pattern optimization in the Shule River Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2016, 35(3):791-799. ] | |
| [4] | 付扬军, 师学义, 和娟. 汾河流域景观破碎化时空演变特征[J]. 自然资源学报, 2019, 34(8):1606-1619. |
| [ Fu Yangjun, Shi Xueyi, He Juan. Spatial-temporal evolution of landscape fragmentation in Fenhe River Basin[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2019, 34(8):1606-1619. ] | |
| [5] | 王晓峰, 延雨, 李月皓, 等. 银川市湿地景观演变及其驱动因素[J]. 干旱区研究, 2021, 5(7):1-14. |
| [ Wang Xiaofeng, Yan Yu, Li Yuehao, et al. Wetland landscape evolution and its driving factors in Yinchuan[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2021, 5(7):1-14. ] | |
| [6] | 黄犁, 徐丽萍. 玛纳斯河流域绿洲时空演变及其景观格局变化[J]. 干旱区研究, 2019, 36(5):1261-1269. |
| [ Huang Li, Xu Liping. Spatiotemporal evolution of the oasis and change of landscape pattern in the Manas River Basin[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2019, 36(5):1261-1269. ] | |
| [7] |
Wei W J, Wang B, Niu X. Soil erosion reduction by grain for green project in desertification areas of northern China[J]. Forests, 2020, 11(4):473.
doi: 10.3390/f11040473 |
| [8] |
Pătru-Stupariu I, Stupariu M, Stoicescu I, et al. Integrating geo-biodiversity features in the analysis of landscape patterns[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2017, 80:363-375.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2017.05.010 |
| [9] | 石玉琼, 王宁练, 李团胜, 等. 榆林市景观生态风险及其时空分异[J]. 干旱区研究, 2019, 36(2):494-504. |
| [ Shi Yuqiong, Wang Ninglian, Li Tuansheng, et al. Landscape ecological risk and its spatial and temporal variation in Yulin City[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2019, 36(2):494-504. ] | |
| [10] |
Wei L, Luo Y, Wang M, et al. Essential fragmentation metrics for agricultural policies: Linking landscape pattern, ecosystem service and land use management in urbanizing China[J]. Agricultural Systems, 2020, 182:102833.
doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2020.102833 |
| [11] | 时卉, 杨兆萍, 韩芳, 等. 干旱区高山湿地生态风险时空变化——以巴音布鲁克自然遗产地为例[J]. 干旱区研究, 2015, 32(3):614-621. |
| [ Shi Hui, Yang Zhaoping, Han Fang, et al. Analysis of ecological risk temporal-spatial change in Arid Alpine Wetland: A case study of Bayanbulak World Natural Heritage Site[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2015, 32(3):614-621. ] | |
| [12] | 梁晓玉, 古元阳, 刘昌, 等. 空间尺度对地形异质性-物种多样性关系的影响: 粒度和幅度[J]. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(2):577-585. |
| [ Liang Xiaoyu, Gu Yuanyang, Liu Chang, et al. The effect of spatial scale on the relationship between topographic heterogeneity and species diversity: Granularity and magnitude[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2021, 40(2):577-585. ] | |
| [13] | 巫丽芸, 何东进, 游巍斌, 等. 东山岛海岸带景观破碎化时空梯度分析[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(3):1055-1064. |
| [ Wu Liyun, He Dongjin, You Weibin, et al. Spatiotemporal gradient analysis of landscape fragmentation in Dongshan Island[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(3):1055-1064. ] | |
| [14] | 刘吉平, 高佳, 董春月. 1954—2015年三江平原沼泽湿地变化的区域分异及影响因素[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(13):4821-4831. |
| [ Liu Jiping, Gao Jia, Dong Chunyue. Regional differentiation and influencing factors of marsh wetland change in Sanjiang Plain during 1954-2015[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(13):4821-4831. ] | |
| [15] | 张秀霞, 颉耀文, 卫娇娇, 等. 1986—2015年干旱区敦煌绿洲景观的时空演变过程[J]. 干旱区研究, 2017, 34(3):669-676. |
| [ Zhang Xiuxia, Xie Yaowen, Wei Jiaojiao, et al. Spatiotemporal evolution of landscapes in the Arid Dunhuang Oasis during the period of 1986-2015[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2017, 34(3):669-676. ] | |
| [16] | 侯蒙京, 高金龙, 葛静, 等. 青藏高原东部高寒沼泽湿地动态变化及其驱动因素研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(1):13-27. |
| [ Hou Mengjing, Gao Jinlong, Ge Jing, et al. An analysis of dynamic changes and their driving factors in marsh wetlands in the eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(1):13-27. ] | |
| [17] | 牛振国, 宫鹏, 程晓, 等. 中国湿地初步遥感制图及相关地理特征分析[J]. 中国科学D辑: 地球科学, 2009, 39(2):188-203. |
| [ Niu Zhenguo, Gong Peng, Cheng Xiao, et al. Analysis of remote sensing mapping and related geographical characteristics of wetland in China[J]. Scientia Sincia (Terrae), 2009, 39(2):188-203. ] | |
| [18] | 陈宜瑜. 中国湿地研究[M]. 长春: 吉林科学技术出版社, 1995: 44. |
| [ Chen Yiyu. Wetland Research in China[M]. Changchun: Jilin Science and Technology Press, 1995: 44. ] | |
| [19] | 周亚军, 刘廷玺, 段利民, 等. 锡林河流域上游河谷湿地景观格局演变及其驱动力[J]. 干旱区研究, 2020, 37(3):580-590. |
| [ Zhou Yajun, Liu Yanxi, Duan Limin, et al. Driving force analysis and landscape pattern evolution in the up stream valley of Xilin River Basin[J]. Journal of Arid Zone Research, 2020, 37(3):580-590. ] | |
| [20] |
Xiao F, Gao G, Shen Q, et al. Spatio-temporal characteristics and driving forces of landscape structure changes in the middle reach of the Heihe River Basin from 1990 to 2015[J]. Landscape Ecology, 2019, 34(4):755-770.
doi: 10.1007/s10980-019-00801-2 |
| [21] | 郑新奇, 付梅臣. 景观格局空间分析技术及其应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010. |
| [ Zheng Xinqi, Fu Meichen. Spatial Analysis Technology of Landscape Pattern and Its Application[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2010. ] | |
| [22] | 刘梦洋, 王小军, 柯杭, 等. 甘肃省陇东地区夏季极端降水及典型年环流特征分析[J]. 干旱区研究, 2021, 38(3):775-784. |
| [ Liu Mengyang, Wang Xiaojun, Ke Hang, et al. Analysis of extreme summer precipitation characteristics and typical years’ circulation characteristics in Longdong Region[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2021, 38(3):775-784. ] | |
| [23] | 王根绪, 李元寿, 王一博, 等. 近40年来青藏高原典型高寒湿地系统的动态变[J]. 地理学报, 2007, 74(5):481-491. |
| [ Wang Genxu, Li Yuanshou, Wang Yibo, et al. Typical alpine wetland systems changes on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in recent 40 years[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2007, 74(5):481-491. ] | |
| [24] | 孙鸿超, 张正祥. 吉林省松花江流域景观格局脆弱性变化及其驱动力[J]. 干旱区研究, 2019, 36(4):1005-1014. |
| [ Sun Hongchao, Zhang Zhengxiang. Changes and driving forces of landscape pattern vulnerability in Songhua River Basin, Jilin Province[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2019, 36(4):1005-1014. ] | |
| [25] | 黄越, 程静, 王鹏. 中国北方农牧交错区生态脆弱性时空演变格局与驱动因素——以盐池县为例[J]. 干旱区地理, 2021, 44(4):1175-1185. |
| [ Huang Yue, Cheng Jing, Wang Peng. Spatio-temporal evolution pattern and driving factors of ecological vulnerability in agriculture-pastoral ecotone in northern China: A case study of Yanchi County[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2021, 44(4):1175-1185. ] | |
| [26] | 文广超, 赵梅娟, 谢洪波, 等. 伊犁河谷西部土地植被覆盖演化及驱动力分析[J]. 干旱区研究, 2021, 38(3):843-854. |
| [ Wen Guangchao, Zhao Meijuan, Xie Hongbo, et al. Analysis of land vegetation cover evolution and driving forces in the western part of the Ili River Valley[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2021, 38(3):843-854. ] | |
| [27] |
赵杰, 杜自强, 武志涛, 等. 中国温带昼夜增温的季节性变化及其对植被动态的影响[J]. 地理学报, 2018, 73(3):395-404.
doi: 10.11821/dlxb201803001 |
|
[ Zhao Jie, Du Ziqiang, Wu Zhitao, et al. Seasonal variations of day and nighttime warming and their effects on vegetation dynamics in China’s temperate zone[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2018, 73(3):395-404. ]
doi: 10.11821/dlxb201803001 |
|
| [28] | 杜际增, 王根绪, 杨燕, 等. 长江黄河源区湿地分布的时空变化及成因[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(18):6173-6182. |
| [ Du Jizeng, Wang Genxu, Yang Yan, et al. Temporal and spatial variation of the distributive patterns and driving force analysis in the Yangtze River and Yellow River source regions wetland[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(18):6173-6182. ] | |
| [29] | 王泉泉, 王行, 张卫国, 等. 滇西北高原湿地景观变化与人为、自然因子的相关性[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(2):726-738. |
| [ Wang Quanquan, Wang Hang, Zhang Weiguo, et al. The correlation between wetland landscape and social-natural factors on Northwestern Yunnan[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(2):726-738. ] | |
| [30] | 康满萍, 赵成章, 白雪, 等. 苏干湖湿地植被覆盖度时空变化格局[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(9):2975-2984. |
| [ Kang Manping, Zhao Chenghang, Bai Xue, et al. The temporal and spatial variation pattern of vegetation coverage in Sugan Lake wetland[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(9):2975-2984. ] | |
| [31] | 周梅, 张飞, 王娟, 等. 新疆艾比湖流域景观格局尺度效应[J]. 干旱区研究, 2017, 34(5):1184-1195. |
| [ Zhou Mei, Zhang Fei, Wang Juan, et al. Effect of landscape pattern scale in the Ebinur Lake Watershed, Xinjiang[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2017, 34(5):1184-1195. ] | |
| [32] | 赵成章, 龙瑞军, 马永欢, 等. 草地产权制度对过度放牧的影响——以肃南县红石窝乡的调查为例[J]. 草业学报, 2005, 16(1):1-5. |
| [ Zhao Chengzhang, Long Ruijun, Ma Yongxin, et al. The impact of the institution of grassland property right on overgrazing: A case from Hongshiwo county Gansu[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2005, 16(1):1-5. ] |
| [1] | 张文睿, 孙栋元, 王亦可, 杨俊, 兰立军, 靳虎甲, 徐裕. 河西走廊水资源-生态环境-社会经济系统耦合关系及时空分异[J]. 干旱区研究, 2024, 41(9): 1527-1537. |
| [2] | 李可璇, 张蕾, 李豪, 张恩月, 李育桢, 宋彩云, 刘庚. 基于MSPA模型和电路理论的晋西北国土空间生态修复关键区域识别[J]. 干旱区研究, 2024, 41(9): 1593-1604. |
| [3] | 高鹏程, 岳艳妮, 鄢继选, 王世杰, 别强. 甘南藏族自治州土地利用与生态风险时空演变及驱动因素[J]. 干旱区研究, 2024, 41(7): 1140-1152. |
| [4] | 菅政博, 罗浩, 单娜娜. “双碳”目标下新疆“三生”空间时空演变特征及碳效应[J]. 干旱区研究, 2024, 41(7): 1238-1248. |
| [5] | 蔡玉琴, 祁栋林, 王烈福, 李海凤, 张德琴. 青海省不同等级寒冷日数时空演变特征[J]. 干旱区研究, 2024, 41(5): 742-752. |
| [6] | 高雅玉, 宋玉, 赵廷红, 高金芳, 何文博, 李泽霞. 马莲河下游产水量时空演变特征[J]. 干旱区研究, 2024, 41(5): 776-787. |
| [7] | 李文秀, 燕振刚. 基于地理探测器的甘肃农牧交错带土地利用时空演化及其驱动机制[J]. 干旱区研究, 2024, 41(4): 590-602. |
| [8] | 陶际峰, 包玉龙, 郭恩亮, 金额尔德木吐, 呼斯乐, 包玉海. 近40 a内蒙古冬旱时空演变特征[J]. 干旱区研究, 2024, 41(3): 387-398. |
| [9] | 孙玮婕, 乔斌, 于红妍, 赵彤, 陈奇. 基于活力-组织力-恢复力的黑河源区高寒湿地景观生态健康评估[J]. 干旱区研究, 2024, 41(2): 301-313. |
| [10] | 邹易, 蒙吉军. 干旱区绿洲-城镇-荒漠景观演变及生态环境效应[J]. 干旱区研究, 2023, 40(6): 988-1001. |
| [11] | 吴玥葶, 郭利丹, 井沛然, 黄峰, 王浩轩. 中亚五国水-能源-粮食-生态耦合关系及时空分异[J]. 干旱区研究, 2023, 40(4): 573-582. |
| [12] | 王鹏, 秦思彤, 胡慧蓉. 近30 a拉萨河流域土地利用变化和生境质量的时空演变特征[J]. 干旱区研究, 2023, 40(3): 492-503. |
| [13] | 黄莹, 王素艳, 马阳, 王岱, 张雯, 王璠. 宁夏近60 a寒潮变化特征及其环流异常[J]. 干旱区研究, 2023, 40(11): 1718-1728. |
| [14] | 党慧, 荣丽华, 李伊彤, 赵名君. 农牧交错区三生空间时空演变特征与影响因素——以内蒙古呼和浩特市为例[J]. 干旱区研究, 2023, 40(10): 1698-1706. |
| [15] | 张志高, 孙梓欣, 张秀丽, 郭可欣, 李卓娅, 郝海姣, 蔡茂堂. 1960—2020年黄河流域气候生长季时空演变及成因分析[J]. 干旱区研究, 2023, 40(10): 1537-1546. |
|
||