
Arid Zone Research ›› 2024, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (8): 1373-1384.doi: 10.13866/j.azr.2024.08.11
• Plant Ecology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2024-03-06
Revised:2024-04-21
Online:2024-08-15
Published:2024-08-22
Contact:
HAO Lina
E-mail:2022020006@stu.cdut.edu.cn;hao_ln@qq.com
WU Siyuan, HAO Lina. Changes in vegetation cover and driving factors in the Yellow River Basin from 2001 to 2021[J].Arid Zone Research, 2024, 41(8): 1373-1384.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Tab. 1
Guidelines for vegetation cover-driven zoning in the Yellow River Basin"
| 驱动因素类型 | 分区准则 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rndvi-t | Rndvi-p | Rndvi-g | Rndvi-tpg | |
| 降水、气温因素驱动 | t>t0.05 | F>F0.05 | ||
| t>t0.05 | F>F0.05 | |||
| t>t0.05 | t>t0.05 | F>F0.05 | ||
| GDP因素驱动 | t>t0.05 | F>F0.05 | ||
| 降水、气温和GDP 因素共同驱动 | t>t0.05 | t>t0.05 | F>F0.05 | |
| t>t0.05 | t>t0.05 | F>F0.05 | ||
| t>t0.05 | t>t0.05 | t>t0.05 | F>F0.05 | |
| t≤t0.05 | t≤t0.05 | t≤t0.05 | F>F0.05 | |
| 未通过显著性检验区 | F≤F0.05 | |||
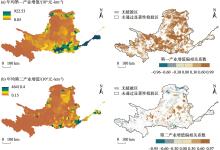
Fig. 9
Spatial distribution of the average annual value-added of the primary industry, the partial correlation coefficient between NDVI and the average annual value-added of the primary industry (a), the average annual value-added of the secondary industry, and the partial correlation coefficient between NDVI and the average annual value-added of the secondary industry (b) in the Yellow River Basin from 2001 to 2021"

| [1] | 辛雨. 2022年度全球气候状况报告发布[N]. 中国科学报, 2023-03-21(001). |
| [ Xin Yu. Global Climate Status Report 2022 Released[N]. China Science Daily, 2023-03-21(001). ] | |
| [2] | 李霞, 王孝康, 刘秀花, 等. 2000—2020年陕西省植被NDVI时空变化及气候因子探测[J]. 水土保持研究, 2024, 31(2): 1-11. |
| [ Li Xia, Wang Xiaokang, Liu Xiuhua, et al. Spatiotemporal variation of vegetation NDVI and climate factor detection in Shaanxi Province from 2000-2020[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2024, 31(2): 1-11. ] | |
| [3] | 赖金林, 齐实, 廖瑞恩, 等. 2000—2019年西南高山峡谷区植被变化对气候变化和人类活动的响应[J]. 农业工程学报, 2023, 39(14): 155-163. |
| [ Lai Jinlin, Qi Shi, Liao Rui’en, et al. Vegetation change responses to climate change and human activities in southwest alpine canyon areas of China from 2000 to 2019[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2023, 39(14): 155-163. ] | |
| [4] | 刘海, 刘凤, 郑粮. 气候变化及人类活动对黄河流域植被覆盖变化的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2021, 35(4): 143-151. |
| [ Liu Hai, Liu Feng, Zheng Liang. Effects of climate change and human activities on vegetation cover change in the Yellow River Basin[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2021, 35(4): 143-151. ] | |
| [5] | 吴姗薇. 影响植被覆盖变化驱动因子的研究综述[J]. 科技视界, 2019(27): 103-106. |
| [ Wu Shanwei. A review on the vegetation cover change and its driving factors[J]. Science and Technology Vision, 2019(27): 103-106. ] | |
| [6] |
马启民, 贾晓鹏, 王海兵, 等. 气候和人为因素对植被变化影响的评价方法综述[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(6): 48-55.
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2019.00004 |
| [15] | [ Wang Yichen, He Jie, He Liang, et al. Vegetation phenology and its response to climate change in the Yellow River Basin from 2001 to 2020[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2024, 44(2): 1-14. ] |
| [16] | 李敏, 张艳. 黄河流域中段植被覆盖时空变化特征及影响因素分析[J]. 贵州师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 41(1): 10-20. |
| [ Li Ming, Zhang Yan. Temporal and spatial variation characteristics and influencing factors of vegetation cover in the middle Yellow River Basin[J]. Journal of Guizhou Normal University (Natural Sciences), 2023, 41(1): 10-20. ] | |
| [17] | 魏潇, 张立峰, 何毅, 等. 2000—2020年黄河流域不同植被类型时空变化特征及其影响因素[J/OL]. 自然资源遥感. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/10.1759.p.20230830.1130.010.html, 2023-08-31. |
| [ Wei Xiao, Zhang Lifeng, He Yi, et al. Spatial and temporal variation characteristics of different vegetation types in Yellow River Basin and their influencing factors from 2000 to 2020[J/OL]. Remote Sensing for Natural Resources. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/10.1759.p.20230830.1130.010.html, 2023-08-31. ] | |
| [18] | 张乐艺, 李霞, 冯京辉, 等. 2000—2018年黄河流域NDVI时空变化及其对气候和人类活动的双重响应[J]. 水土保持通报, 2021, 41(5): 276-286. |
| [ Zhang Leyi, Li Xia, Feng Jinghui, et al. Spatial-temporal changes of NDVI in Yellow River basin and its dual response to climate change and human activities during 2000-2018[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2021, 41(5): 276-286. ] | |
| [19] | 焦士兴, 林璐霜, 王安周, 等. 黄河流域9省区经济发展、产业结构与环境污染关系[J/OL]. 华北水利水电大学学报(自然科学版). http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/41.1432.TV.20231204.0916.002.html, 2023-12-04. |
| [ Jiao Shixing, Lin Lushuang, Wang Anzhou, et al. Relationship among the economic development, industrial structure and environmental pollution in the nine provincial regions of the Yellow River Basin[J/OL]. Journal of North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power(Natural Science Edition). http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/41.1432.TV.20231204.0916.002.html, 2023-12-04. ] | |
| [20] |
丁金宏, 程晨, 张伟佳, 等. 胡焕庸线的学术思想源流与地理分界意义[J]. 地理学报, 2021, 76(6): 1317-1333.
doi: 10.11821/dlxb202106001 |
|
[ Ding Jinhong, Cheng Chen, Zhang Weijia, et al. The ideological origins and geographical demarcation significance of Hu Huanyong Line[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2021, 76(6): 1317-1333. ]
doi: 10.11821/dlxb202106001 |
|
| [6] |
[ Ma Qimin, Jia Xiaopeng, Wang Haibing, et al. Recent advances in driving mechanisms of climate and anthropogenic factors on vegetation change[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(6): 48-55. ]
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2019.00004 |
| [7] |
何远政, 黄文达, 赵昕, 等. 气候变化对植物多样性的影响研究综述[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(1): 59-66.
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2020.00104 |
|
[ He Yuanzheng, Huang Wenda, Zhao Xin, et al. Review on the impact of climate change on plant diversity[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(1): 59-66. ]
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2020.00104 |
|
| [8] |
Gao J B, Jiao K W, Wu S H. Investigating the spatially heterogeneous relationships between climate factors and NDVI in China during 1982 to 2013[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2019, 29(10): 1597-1609.
doi: 10.1007/s11442-019-1682-2 |
| [9] |
路建兵, 鞠珂, 廖伟斌. 2000—2020年甘肃省植被覆盖特征及其对气候变化和人类活动的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(4): 118-127.
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2022.00162 |
|
[ Lu Jianbing, Ju Ke, Liao Weibin. Variation in NDVI and its response to climate change and human activities in Gansu Province during 2000-2020[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(4): 118-127. ]
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2022.00162 |
|
| [10] | Han G F, Xu J H. Influence of population and economic development on vegetation: A case study in Chongqing City[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2008, 17(5): 785-792. |
| [11] | 张勇. 黄河流域生态保护和高质量发展研究[J]. 农业科技与信息, 2023(11): 77-80. |
| [ Zhang Yong. Research on ecological protection and high quality development of the Yellow River Basin[J]. Agricultural Science Technology and Information, 2023(11): 77-80. ] | |
| [12] | 李海生. 黄河流域生态环境问题系统识别与展望[J]. 环境科学研究, 2024, 37(1): 1-10. |
| [ Li Haisheng. Systematic identification and prospect of eco-environmental problems in the Yellow River Basin[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2024, 37(1): 1-10. ] | |
| [21] | Peng S Z, Ding Y X, Liu W Z, et al. 1 km monthly temperature and precipitation dataset for China from 1901 to 2017[J]. Earth System Science Data, 2019, 11(4): 1931-1946. |
| [22] | 陈春波, 李均力, 赵炎, 等. 新疆草地时空动态及其对气候变化的响应——以昌吉回族自治州为例[J]. 干旱区研究, 2023, 40(9): 1484-1497. |
| [ Chen Chunbo, Li Junli, Zhao Yan, et al. Spatiotemporal dynamics of grassland vegetation and its responses to climate change in Changji Hui Autonomous Prefecture, Xinjiang[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2023, 40(9): 1484-1497. ] | |
| [23] | 徐虹, 刘琴. 2001—2019年云南省植被NDVI变化及其气候因子的关系[J]. 水土保持研究, 2022, 29(1): 162-168. |
| [ Xu Hong, Liu Qin. Analysis of vegetation NDVI dynamic and its relationship with climatic factors in Yunnan Province during 2001-2019[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2022, 29(1): 162-168. ] | |
| [24] | 吴万民, 刘涛, 陈鑫. 西北干旱半干旱区NDVI季节性变化及其影响因素[J]. 干旱区研究, 2023, 40(12): 1969-1981. |
| [ Wu Wanmin, Liu Tao, Chen Xin. Seasonal changes of NDVI in the arid and semi-arid regions of Northwest China and its influencing factors[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2023, 40(12): 1969-1981. ] | |
| [25] | Pei Z F, Fang S B, Yang W N, et al. The relationship between NDVI and Climate factors at different monthly time scales: A case study of grasslands in inner Mongolia, China (1982-2015)[J]. Sustainability, 2019, 11(24): 7243. |
| [26] | Wang H J, Li Z, Niu Y, et al. Evolution and climate drivers of NDVI of natural vegetation during the growing season in the arid region of Northwest China[J]. Forests, 2022, 13(7): 1082. |
| [27] | 赵雨琪, 魏天兴. 1990—2020年黄土高原典型县域植被覆盖变化及影响因素[J]. 干旱区研究, 2024, 41(1): 147-156. |
| [ Zhao Yuqi, Wei Tianxing. Changes in vegetation cover and influencing factors in typical counties of the Loess Plateau from 1990 to 2020[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2024, 41(1): 147-156. ] | |
| [28] | 谢胜金, 刘永和, 姚风欣. 1998—2015年北京市NDVI时空变化及其与气候因子的响应关系[J]. 水土保持研究, 2020, 27(3): 190-196. |
| [ Xie Shengjin, Liu Yonghe, Yao Fengxin. Spatial-temporal characteristics of NDVI and its relationship with climate change in Beijing from 1998 to 2015[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 27(3): 190-196. ] | |
| [29] | 王永财, 孙艳玲, 王中良. 1998—2011年海河流域植被覆盖变化及气候因子驱动分析[J]. 资源科学, 2014, 36(3): 594-602. |
| [ Wang Yongcai, Sun Yanling, Wang Zhongliang. Spatial-temporal change in vegetation cover and climate factor drivers of variation in the Haihe River Basin 1998-2011[J]. Resources Science, 2014, 36(3): 594-602. ] | |
| [30] | 石悦樾, 银正彤, 郑文锋. 基于MODIS数据乌江流域植被覆盖变化与气候变化关系研究[J]. 林业资源管理, 2017(1): 127-134. |
| [ Shi Yueyue, Yin Zhengtong, Zhen Wenfeng. Study on the response of vegetation cover change and climate change in Wujiang River Basin based on MODIS data[J]. Forest Resources Management, 2017(1): 127-134. ] | |
| [31] | 陈云浩, 李晓兵, 史培军. 1983—1992年中国陆地NDVI变化的气候因子驱动分析[J]. 植物生态学报, 2001, 25(6): 716-720. |
| [ Chen Yunhao, Li Xiaobing, Shi Peijun. Variation in NDVI Driven by climate factorsacross China, 1983-1992[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2001, 25(6): 716-720. ] | |
| [32] |
孙高鹏, 刘宪锋, 王小红, 等. 2001—2020年黄河流域植被覆盖变化及其影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(4): 205-212.
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2021.00076 |
|
[ Sun Gaopeng, Liu Xianfeng, Wang Xiaohong, et al. Changes in vegetation coverage and its influencing factors across the Yellow River Basin during 2001-2020[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(4): 205-212. ]
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2021.00076 |
|
| [33] | Ren Y Q, Liu J P, Liu S X, et al. Effects of climate change on vegetation growth in the Yellow River Basin from 2000 to 2019[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(687): 687. |
| [34] | 闫奕飞, 白强, 孙虎, 等. 黄河流域植被变化和产水服务的时空特征分析[J]. 水土保持学报, 2024, 38(1): 1-10. |
| [ Yan Yifei, Bai Qiang, Sun Hu, et al. Analysis of spatio-temporal characteristic of vegetation cover and water production services in the Yellow River Basin[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2024, 38(1): 1-10. ] | |
| [35] | 杨丹, 王晓峰. 黄土高原气候和人类活动对植被NPP变化的影响[J]. 干旱区研究, 2022, 39(2): 584-593. |
| [ Yang Dan, Wang Xiaofeng. Contribution of climatic change and human activities to changes in net primary productivity in the Loess Plateau[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2022, 39(2): 584-593. ] | |
| [36] |
张志强, 刘欢, 左其亭, 等. 2000—2019年黄河流域植被覆盖度时空变化[J]. 资源科学, 2021, 43(4): 849-858.
doi: 10.18402/resci.2021.04.18 |
|
[ Zhang Zhiqiang, Liu Huan, Zuo Qiting, et al. Spatiotemporal change of fractional vegetation cover in the Yellow River Basin during 2000-2019[J]. Resources Science, 2021, 43(4): 849-858. ]
doi: 10.18402/resci.2021.04.18 |
|
| [37] | Jian S Q, Zhang Q K, Wang H L. Spatial-temporal trends in and attribution analysis of vegetation change in the Yellow River Basin, China[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14: 4607. |
| [38] | 王一, 郝利娜, 许强, 等. 2001—2019年黄土高原植被覆盖度时空演化特征及地理因子解析[J]. 生态学报, 2023, 43(6): 2397-2407. |
| [ Wang Yi, Hao Lina, Xu Qiang, et al. Spatio-temporal variations of vegetation coverage and its geographical factors analysis on the Loess Plateau from 2001 to 2019[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2023, 43(6): 2397-2407. ] | |
| [39] | 郭帅, 裴艳茜, 胡胜, 等. 黄河流域植被指数对气候变化的响应及其与水沙变化的关系[J]. 水土保持通报, 2020, 40(3): 1-7. |
| [ Guo Shuai, Pei Yanqian, Hu Sheng, et al. Response of vegetation index to climate change and their relationship with runoff sediment change in Yellow River Basin[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 40(3): 1-7. ] | |
| [13] | 赵倩倩, 李建华, 张桂琴, 等. 气候变化背景下黄河流域植被变化及其成因[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2022, 27(1): 157-169. |
| [ Zhao Qianqian, Li Jianhua, Zhang Guiqin, et al. Vegetation changes and their causes in the Yellow River Basin under the background of climate change[J]. Climatic and Environmental Research, 2022, 27(1): 157-169. ] | |
| [14] | 解晗, 同小娟, 李俊, 等. 2000—2018年黄河流域生长季植被指数变化及其对气候因子的响应[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(11): 4536-4549. |
| [ Xie Han, Tong Xiaojuan, Li Jun, et al. Changes of NDVI and EVI and their responses to climatic variables in the Yellow River Basin during the growing season of 2000-2018[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(11): 4536-4549. ] | |
| [15] | 王祎宸, 贺洁, 何亮, 等. 黄河流域2001—2020年植被物候及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 生态学报, 2024, 44(2): 1-14. |
| [40] | 李建飞, 李小兵, 周义. 2000—2015年乌兰察布市生长季NDVI时空变化及其影响因素[J]. 干旱区研究, 2019, 36(5): 1238-1249. |
| [ Li Jianfei, Li Xiaobing, Zhou Yi. Spatiotemporal variation of NDVI and its affecting factors in Ulanqab City in growing season from 2000 to 2015[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2019, 36(5): 1238-1249. ] | |
| [41] | 刘育坤, 刘晓波, 孙亚丽, 等. 基于RS与GIS的呼和浩特市植被覆盖度变化分析[J]. 内蒙古科技与经济, 2020(7): 47-50. |
| [ Liu Yukun, Liu Xiaobo, Sun Yali, et al. Analysis of vegetation coverage change in Hohhot City based on RS and GIS[J]. Inner Mongolia Science Technology & Economy, 2020(7): 47-50. ] | |
| [42] | 何妮, 姚聪莉, 张畅. “双碳”目标下黄河流域农业生态效率的动态演进与收敛特征[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(社会科学版), 2024, 24(3): 149-160. |
| [ He Ni, Yao Congli, Zhang Chang. Dynamic evolution and convergence characteristics of agricultural ecological efficiency in the Yellow River Basin under the “Dual Carbon” Goal[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Social Science Edition), 2024, 24(3): 149-160. ] | |
| [43] | 周锡饮, 师华定, 王秀茹. 气候变化和人类活动对蒙古高原植被覆盖变化的影响[J]. 干旱区研究, 2014, 31(4): 604-610. |
| [ Zhou Xiyin, Shi Huading, Wang Xiuru. Impact of climate change and human activities on vegetation coverage in the Mongolian Plateau[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2014, 31(4): 604-610. ] | |
| [44] |
赵安周, 田新乐. 基于GEE平台的1986—2021年黄土高原植被覆盖度时空演变及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2124-2133.
doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.11.003 |
| [ Zhao Anzhou, Tian Xinle. Spatiotemporal evolution and influencing factors of vegetation coverage in the Loess Plateau from 1986 to 2021 based on GEE platform[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2022, 31(11): 2124-2133. ] | |
| [45] | 韩素娟. “一带一路”背景下青海省产业结构转型升级研究[J]. 青海民族研究, 2021, 32(1): 179-185. |
| [ Han Sujuan. The research of the transformation and upgrading of industry structure of Qinghai Province under the background of one Belt and Road initiative[J]. Nationalities Research in Qinghai, 2021, 32(1): 179-185. ] | |
| [46] | 许强. 内蒙古煤炭经济发展问题及其策略研究[J]. 内蒙古煤炭经济, 2023(21): 114-116. |
| [ Xu Qiang. Research on the development of coal economy in Inner Mongolia and its strategies[J]. Inner Mongolia Coal Economy, 2023(21): 114-116. ] | |
| [47] |
马丽, 田华征, 康蕾. 黄河流域矿产资源开发的生态环境影响与空间管控路径[J]. 资源科学, 2020, 42(1): 137-149.
doi: 10.18402/resci.2020.01.14 |
|
[ Ma Li, Tian Huazheng, Kang Lei. Eco-environmental impact and spatial control of mineral resources exploitation in the Yellow River Basin[J]. Resources Science, 2020, 42(1): 137-149. ]
doi: 10.18402/resci.2020.01.14 |
|
| [48] | 焦晓亮, 田金梅, 周永利. 黄河流域露天矿排土场生态修复评价[J]. 煤炭工程, 2020, 52(S2): 74-79. |
| [ Jiao Xiaoliang, Tian Jinmei, Zhou Yongli. Ecological restoration evaluation of coalmine dumps in Yellow River Basin[J]. Coal Engineering, 2020, 52(S2): 74-79. ] | |
| [49] | 陈静. 黄河流域煤矿区生物多样性的保护与恢复——以神东矿区为例[J/OL]. 煤炭工程. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.4658.td.20231225.1623.002, 2023-12-28. |
| [ Chen Jing. Conservation and restoration of biodiversity in coal mining areas of the Yellow River Basin: A case study of Shendong mining area[J/OL]. Coal Engineering. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.4658.td.20231225.1623.002, 2023-12-28. ] |
|
||
