
Arid Zone Research ›› 2021, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (6): 1771-1781.doi: 10.13866/j.azr.2021.06.29
• Ecology and Environment • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZENG Hongxia( ),ZHAO Chengzhang(
),ZHAO Chengzhang( ),WANG Yufang,LI Xiaoya,ZHAO Tingting,TANG Yurui
),WANG Yufang,LI Xiaoya,ZHAO Tingting,TANG Yurui
Received:2021-02-09
Revised:2021-04-02
Online:2021-11-15
Published:2021-11-29
Contact:
Chengzhang ZHAO
E-mail:376948155@qq.com;zhaocz@nwnu.edu.cn
ZENG Hongxia,ZHAO Chengzhang,WANG Yufang,LI Xiaoya,ZHAO Tingting,TANG Yurui. Landscape pattern evolution and its influencing factors of alpine wetland in Yanchi Bay[J].Arid Zone Research, 2021, 38(6): 1771-1781.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Tab. 1
Interpretation sign of Yanchi Bay alpine wetland"
| 湿地类 | 湿地型 | 景观特征 | 影像特征 | 543波段组合显示 | 实地图片 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 沼泽湿地 | 草本沼泽 | 水生和沼生的草本植物组成优势群落的淡水沼泽,主要生长杉叶藻、中间型荸荠和海韭菜 | 呈片状分布,形状不规则,呈黑红色,影纹不均、粗糙 |  |  |
| 内陆盐沼 | 生长碱地风毛菊、芨芨草、赖草等盐生植被的沼泽,以苏打、氯化物和硫酸盐为主的盐土 | 呈片状杂乱分布,形状不规则,呈粉红色、青色,影纹粗糙伴有红黑点 | 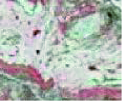 |  | |
| 沼泽化草甸 | 地势低洼、排水不畅、土壤过分潮湿、通透性不良等环境条件下发育,有早熟禾、苔草和嵩草等植物 | 呈片状、大块分布,形状不规则,呈红色,影纹不均 |  |  | |
| 裸斑 | 受强烈的蒸发作用,盐分在地表集聚,无生长植被,呈白色 | 边界清晰,形状规则,呈白色,影纹不均 |  |  | |
| 河流湿地 | 永久性河流湿地 | 有明显泥沙淤积、河道以及水流痕迹 | 常呈条带状分布,边界清晰,呈绿色、浅绿色,影纹较均匀 | 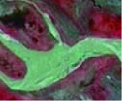 |  |
Tab. 2
Computational formula of landscape index and ecological significance"
| 景观指数 | 计算公式 | 生态学意义 |
|---|---|---|
| 斑块面积 | | 其大小反映了物种、能量和养分等信息的差异,值越大表示供给生物所需的物质和能量越多。式中:ai为斑块i的面积。 |
| 斑块数量 | NP=n | 反映了景观的空间格局,其值的大小与景观破碎度呈正相关,NP越大,景观破碎化程度越高。式中:n为某一斑块类型的斑块总个数。 |
| 最大斑块指数 | | 对于景观优势类型等的确定有重要作用,其数值越大,对景观总体的影响越大,优势度也越高,反之亦然。式中:分子为景观中最大斑块的面积;A为斑块总面积。 |
| 斑块密度 | | 反应景观的破碎化程度,值越大说明景观的破碎化程度越大。式中:N为景观中所有的斑块总数,A为总面积。 |
| 形状指数 | | LSI值越小,表明景观的形状越规整;LSI值越大,表明景观的形状趋于复杂。式中:A为总面积,E为景观中所有斑块边界总长度,0.25为正方形校正系数。 |
| 蔓延度指数 | | 其值越高,表明整体景观具有良好的连接性;其值越低,说明景观中连通性不好,破碎化程度较高。式中:m为景观中斑块总数;Pij为斑块类型i与j相邻的概率。 |
| 香浓多样性指数 | | 其值为0时,说明只有一个斑块组成了整个景观,随着SHDI增大,表明景观中不稳定信息在增多,破碎化程度在增大。式中:Pi为景观类型i的斑块占景观所有斑块的比例。 |
Tab. 3
Change table of wetland transfer matrix from 1989 to 2019 /km2"
| 时段 | 景观类型 | 草本沼泽 | 裸斑 | 永久性河流湿地 | 沼泽化草甸 | 内陆盐沼 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1989—2007年 | 草本沼泽 | 6.00 | 2.07 | 2.93 | 9.06 | 7.55 |
| 裸斑 | 1.08 | 3.52 | 7.89 | 0.70 | 3.37 | |
| 永久性河流湿地 | 0.84 | 0.91 | 15.31 | 1.24 | 10.75 | |
| 沼泽化草甸 | 2.72 | 0.68 | 1.13 | 50.38 | 11.44 | |
| 内陆盐沼 | 1.15 | 0.95 | 3.73 | 7.44 | 71.31 | |
| 2007—2019年 | 草本沼泽 | 9.27 | 3.48 | 3.82 | 6.04 | 6.51 |
| 裸斑 | 1.15 | 7.70 | 4.70 | 0.70 | 3.30 | |
| 永久性河流湿地 | 1.44 | 3.26 | 11.08 | 0.76 | 2.38 | |
| 沼泽化草甸 | 10.93 | 1.14 | 3.10 | 48.63 | 13.49 | |
| 内陆盐沼 | 5.06 | 4.21 | 12.68 | 10.13 | 53.43 |
| [1] |
Guo M, Li J, Sheng C, et al. A review of wetland remote sensing[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(4):777.
doi: 10.3390/s17040777 |
| [2] |
Li Z, Jiang W, Wang W, et al. Ecological risk assessment of the wetlands in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2020, 117:106677.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106677 |
| [3] | 潘竟虎, 刘晓. 疏勒河流域景观生态风险评价与生态安全格局优化构建[J]. 生态学杂志, 2016, 35(3):791-799. |
| [ Pan Jinghu, Liu Xiao. Landscape ecological risk assessment and ecological security pattern optimization in the Shule River Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2016, 35(3):791-799. ] | |
| [4] | 付扬军, 师学义, 和娟. 汾河流域景观破碎化时空演变特征[J]. 自然资源学报, 2019, 34(8):1606-1619. |
| [ Fu Yangjun, Shi Xueyi, He Juan. Spatial-temporal evolution of landscape fragmentation in Fenhe River Basin[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2019, 34(8):1606-1619. ] | |
| [5] | 王晓峰, 延雨, 李月皓, 等. 银川市湿地景观演变及其驱动因素[J]. 干旱区研究, 2021, 5(7):1-14. |
| [ Wang Xiaofeng, Yan Yu, Li Yuehao, et al. Wetland landscape evolution and its driving factors in Yinchuan[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2021, 5(7):1-14. ] | |
| [6] | 黄犁, 徐丽萍. 玛纳斯河流域绿洲时空演变及其景观格局变化[J]. 干旱区研究, 2019, 36(5):1261-1269. |
| [ Huang Li, Xu Liping. Spatiotemporal evolution of the oasis and change of landscape pattern in the Manas River Basin[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2019, 36(5):1261-1269. ] | |
| [7] |
Wei W J, Wang B, Niu X. Soil erosion reduction by grain for green project in desertification areas of northern China[J]. Forests, 2020, 11(4):473.
doi: 10.3390/f11040473 |
| [8] |
Pătru-Stupariu I, Stupariu M, Stoicescu I, et al. Integrating geo-biodiversity features in the analysis of landscape patterns[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2017, 80:363-375.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2017.05.010 |
| [9] | 石玉琼, 王宁练, 李团胜, 等. 榆林市景观生态风险及其时空分异[J]. 干旱区研究, 2019, 36(2):494-504. |
| [ Shi Yuqiong, Wang Ninglian, Li Tuansheng, et al. Landscape ecological risk and its spatial and temporal variation in Yulin City[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2019, 36(2):494-504. ] | |
| [10] |
Wei L, Luo Y, Wang M, et al. Essential fragmentation metrics for agricultural policies: Linking landscape pattern, ecosystem service and land use management in urbanizing China[J]. Agricultural Systems, 2020, 182:102833.
doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2020.102833 |
| [11] | 时卉, 杨兆萍, 韩芳, 等. 干旱区高山湿地生态风险时空变化——以巴音布鲁克自然遗产地为例[J]. 干旱区研究, 2015, 32(3):614-621. |
| [ Shi Hui, Yang Zhaoping, Han Fang, et al. Analysis of ecological risk temporal-spatial change in Arid Alpine Wetland: A case study of Bayanbulak World Natural Heritage Site[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2015, 32(3):614-621. ] | |
| [12] | 梁晓玉, 古元阳, 刘昌, 等. 空间尺度对地形异质性-物种多样性关系的影响: 粒度和幅度[J]. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(2):577-585. |
| [ Liang Xiaoyu, Gu Yuanyang, Liu Chang, et al. The effect of spatial scale on the relationship between topographic heterogeneity and species diversity: Granularity and magnitude[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2021, 40(2):577-585. ] | |
| [13] | 巫丽芸, 何东进, 游巍斌, 等. 东山岛海岸带景观破碎化时空梯度分析[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(3):1055-1064. |
| [ Wu Liyun, He Dongjin, You Weibin, et al. Spatiotemporal gradient analysis of landscape fragmentation in Dongshan Island[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(3):1055-1064. ] | |
| [14] | 刘吉平, 高佳, 董春月. 1954—2015年三江平原沼泽湿地变化的区域分异及影响因素[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(13):4821-4831. |
| [ Liu Jiping, Gao Jia, Dong Chunyue. Regional differentiation and influencing factors of marsh wetland change in Sanjiang Plain during 1954-2015[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(13):4821-4831. ] | |
| [15] | 张秀霞, 颉耀文, 卫娇娇, 等. 1986—2015年干旱区敦煌绿洲景观的时空演变过程[J]. 干旱区研究, 2017, 34(3):669-676. |
| [ Zhang Xiuxia, Xie Yaowen, Wei Jiaojiao, et al. Spatiotemporal evolution of landscapes in the Arid Dunhuang Oasis during the period of 1986-2015[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2017, 34(3):669-676. ] | |
| [16] | 侯蒙京, 高金龙, 葛静, 等. 青藏高原东部高寒沼泽湿地动态变化及其驱动因素研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(1):13-27. |
| [ Hou Mengjing, Gao Jinlong, Ge Jing, et al. An analysis of dynamic changes and their driving factors in marsh wetlands in the eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(1):13-27. ] | |
| [17] | 牛振国, 宫鹏, 程晓, 等. 中国湿地初步遥感制图及相关地理特征分析[J]. 中国科学D辑: 地球科学, 2009, 39(2):188-203. |
| [ Niu Zhenguo, Gong Peng, Cheng Xiao, et al. Analysis of remote sensing mapping and related geographical characteristics of wetland in China[J]. Scientia Sincia (Terrae), 2009, 39(2):188-203. ] | |
| [18] | 陈宜瑜. 中国湿地研究[M]. 长春: 吉林科学技术出版社, 1995: 44. |
| [ Chen Yiyu. Wetland Research in China[M]. Changchun: Jilin Science and Technology Press, 1995: 44. ] | |
| [19] | 周亚军, 刘廷玺, 段利民, 等. 锡林河流域上游河谷湿地景观格局演变及其驱动力[J]. 干旱区研究, 2020, 37(3):580-590. |
| [ Zhou Yajun, Liu Yanxi, Duan Limin, et al. Driving force analysis and landscape pattern evolution in the up stream valley of Xilin River Basin[J]. Journal of Arid Zone Research, 2020, 37(3):580-590. ] | |
| [20] |
Xiao F, Gao G, Shen Q, et al. Spatio-temporal characteristics and driving forces of landscape structure changes in the middle reach of the Heihe River Basin from 1990 to 2015[J]. Landscape Ecology, 2019, 34(4):755-770.
doi: 10.1007/s10980-019-00801-2 |
| [21] | 郑新奇, 付梅臣. 景观格局空间分析技术及其应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010. |
| [ Zheng Xinqi, Fu Meichen. Spatial Analysis Technology of Landscape Pattern and Its Application[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2010. ] | |
| [22] | 刘梦洋, 王小军, 柯杭, 等. 甘肃省陇东地区夏季极端降水及典型年环流特征分析[J]. 干旱区研究, 2021, 38(3):775-784. |
| [ Liu Mengyang, Wang Xiaojun, Ke Hang, et al. Analysis of extreme summer precipitation characteristics and typical years’ circulation characteristics in Longdong Region[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2021, 38(3):775-784. ] | |
| [23] | 王根绪, 李元寿, 王一博, 等. 近40年来青藏高原典型高寒湿地系统的动态变[J]. 地理学报, 2007, 74(5):481-491. |
| [ Wang Genxu, Li Yuanshou, Wang Yibo, et al. Typical alpine wetland systems changes on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in recent 40 years[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2007, 74(5):481-491. ] | |
| [24] | 孙鸿超, 张正祥. 吉林省松花江流域景观格局脆弱性变化及其驱动力[J]. 干旱区研究, 2019, 36(4):1005-1014. |
| [ Sun Hongchao, Zhang Zhengxiang. Changes and driving forces of landscape pattern vulnerability in Songhua River Basin, Jilin Province[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2019, 36(4):1005-1014. ] | |
| [25] | 黄越, 程静, 王鹏. 中国北方农牧交错区生态脆弱性时空演变格局与驱动因素——以盐池县为例[J]. 干旱区地理, 2021, 44(4):1175-1185. |
| [ Huang Yue, Cheng Jing, Wang Peng. Spatio-temporal evolution pattern and driving factors of ecological vulnerability in agriculture-pastoral ecotone in northern China: A case study of Yanchi County[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2021, 44(4):1175-1185. ] | |
| [26] | 文广超, 赵梅娟, 谢洪波, 等. 伊犁河谷西部土地植被覆盖演化及驱动力分析[J]. 干旱区研究, 2021, 38(3):843-854. |
| [ Wen Guangchao, Zhao Meijuan, Xie Hongbo, et al. Analysis of land vegetation cover evolution and driving forces in the western part of the Ili River Valley[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2021, 38(3):843-854. ] | |
| [27] |
赵杰, 杜自强, 武志涛, 等. 中国温带昼夜增温的季节性变化及其对植被动态的影响[J]. 地理学报, 2018, 73(3):395-404.
doi: 10.11821/dlxb201803001 |
|
[ Zhao Jie, Du Ziqiang, Wu Zhitao, et al. Seasonal variations of day and nighttime warming and their effects on vegetation dynamics in China’s temperate zone[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2018, 73(3):395-404. ]
doi: 10.11821/dlxb201803001 |
|
| [28] | 杜际增, 王根绪, 杨燕, 等. 长江黄河源区湿地分布的时空变化及成因[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(18):6173-6182. |
| [ Du Jizeng, Wang Genxu, Yang Yan, et al. Temporal and spatial variation of the distributive patterns and driving force analysis in the Yangtze River and Yellow River source regions wetland[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(18):6173-6182. ] | |
| [29] | 王泉泉, 王行, 张卫国, 等. 滇西北高原湿地景观变化与人为、自然因子的相关性[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(2):726-738. |
| [ Wang Quanquan, Wang Hang, Zhang Weiguo, et al. The correlation between wetland landscape and social-natural factors on Northwestern Yunnan[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(2):726-738. ] | |
| [30] | 康满萍, 赵成章, 白雪, 等. 苏干湖湿地植被覆盖度时空变化格局[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(9):2975-2984. |
| [ Kang Manping, Zhao Chenghang, Bai Xue, et al. The temporal and spatial variation pattern of vegetation coverage in Sugan Lake wetland[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(9):2975-2984. ] | |
| [31] | 周梅, 张飞, 王娟, 等. 新疆艾比湖流域景观格局尺度效应[J]. 干旱区研究, 2017, 34(5):1184-1195. |
| [ Zhou Mei, Zhang Fei, Wang Juan, et al. Effect of landscape pattern scale in the Ebinur Lake Watershed, Xinjiang[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2017, 34(5):1184-1195. ] | |
| [32] | 赵成章, 龙瑞军, 马永欢, 等. 草地产权制度对过度放牧的影响——以肃南县红石窝乡的调查为例[J]. 草业学报, 2005, 16(1):1-5. |
| [ Zhao Chengzhang, Long Ruijun, Ma Yongxin, et al. The impact of the institution of grassland property right on overgrazing: A case from Hongshiwo county Gansu[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2005, 16(1):1-5. ] |
|
||