
Arid Zone Research ›› 2025, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (2): 223-235.doi: 10.13866/j.azr.2025.02.04
• Weather and Climate • Previous Articles Next Articles
MA Chao1( ), LIU Yan2, LIU Jing3(
), LIU Yan2, LIU Jing3( ), YANG Lianmei3
), YANG Lianmei3
Received:2024-09-02
Revised:2024-12-10
Online:2025-02-15
Published:2025-02-21
Contact:
LIU Jing
E-mail:sonteryfan@aliyun.com;994365768@qq.com
MA Chao, LIU Yan, LIU Jing, YANG Lianmei. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of cloud water resources in the Tarim Basin in summer[J].Arid Zone Research, 2025, 42(2): 223-235.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
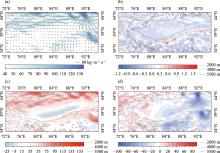
Fig. 3
Distribution of the average water vapor flux (a, vector, unit: kg·m-1·s-1, shade >40 kg·m-1·s-1), water vapor flux divergence (b, unit: 10-5g·m-1·s-1), the zonal water vapor flux (c, unit: kg·m-1·s-1) and the meridional water vapor flux (d, unit: kg·m-1·s-1) in the whole layer in the Tarim Basin in summer from 1979 to 2022"

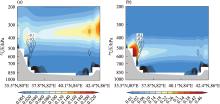
Fig. 7
Vertical profiles of (a) cloud ice water content (unit: 10-1g·m-2) and water vapor flux divergence (unit: 10-5g·m-1·s-1), (b) cloud liquid water content (unit: 10-1g·m-2) and water vapor flux divergence (unit: 10-5g·m-1·s-1) along the blue solid line in Figure 1 in summer from 1979 to 2022"

Tab. 1
Four spatial distribution types of total column water vapor transportation over the Tarim Basin in summer from 1979 to 2022"
| 类型 | 个数/个 | 年份 |
|---|---|---|
| 全区偏多型 | 14 | 1982,1986,1987,1989,1992,1994,1995,1998,2004,2007,2012,2013,2020,2021 |
| 全区偏少型 | 12 | 1980,1984,1985,1988,1990,1991,1999,2000,2008,2011,2015,2018 |
| 西南多东北少型 | 12 | 1979,1981,1983,1997,2001,2002,2003,2006,2009,2010,2017,2019 |
| 西南少东北多型 | 6 | 1996,2005,2014,2016,2018,1993 |
| [1] | 丁贤荣. 高山增水效应及其水资源意义[J]. 山地学报, 2003, 21(6): 681-685. |
| [Ding Xianrong. Water increasing effect of mountains and its value of water resources[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2003, 21(6): 681-685. ] | |
| [2] | 彭宽军, 陈勇航, 林雄, 等. 利用CERES卫星遥感资料研究新疆三大山区低层云水资源[C]// 中国气象学会气候资源应用研究委员会, 国家气候中心. 第26届中国气象学会年会气候资源应用研究分会场论文集, 2009. |
| [Peng Kuanjun, Chen Yonghang, Lin Xiong, et al. CERES satellite remote sensing data were used to study the low-level cloud water resources in the three mountainous areas of Xinjiang[C]// Climate Resources Application Research Committee of Chinese Meteorological Societe, China Climate Center, the 26th Annual Meeting of the Chinese Meteorological Society, 2009. ] | |
| [3] | 张家宝, 袁玉江. 试论新疆气候对水资源的影响[J]. 自然资源学报, 2002, 17(1): 28-34. |
|
[Zhang Jiabao, Yuan Yujiang. A tentative discussion on the impact of climate on surface water resources in Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2002, 17(1): 28-34. ]
doi: 10.11849/zrzyxb.2002.01.005 |
|
| [4] | 陈勇航, 黄建平, 王天河, 等. 西北地区不同类型云的时空分布及其与降水的关系[J]. 应用气象学报, 2005, 16(6): 717-727, 862. |
| [Chen Yonghang, Huang Jianping, Wang Tianhe, et al. Temporal and spatial distribution of the different clouds over northwestern China with the relation to precipitation[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 2005, 16(6): 717-727, 862. ] | |
| [5] | 尹宪志, 王毅荣, 徐文君, 等. 祁连山空中云水资源开发潜力研究新进展[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 2020, 14(6): 134-140. |
| [Yin Xianzhi, Wang Yirong, Xu Wenjun, et al. Recent progress in research on potential for the development of cloud water resources over Qilian Mountains area[J]. Desert and Oasis Meteorology, 2020, 14(6): 134-140. ] | |
| [6] | 余杰, 蔡森, 周毓荃, 等. 2000—2019年西北地区云水资源时空特征研究[J]. 气象学报, 2024, 82(4): 476-489. |
| [Yu Jie, Cai Miao, Zhou Yuquan, et al. Spatiotemporal characteristics of cloud water resources in Northwest China from 2000 to 2019[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2024, 82(4): 476-489. ] | |
| [7] | 李家叶, 李铁键, 王光谦, 等. 空中水资源及其降水转化分析[J]. 科学通报, 2018, 63(26): 2785-2796. |
| [Li Jiaye, Li Tiejian, Wang Guangqian, et al. Atmospheric water resource and precipitation conversion[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2018, 63(26): 2785-2796. ] | |
| [8] | 黄美元. 我国人工降水亟待解决的问题和发展思路[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2011, 16(5): 543-550. |
| [Huang Meiyuan. Urgent problems and thinking of development for precipitation enhancement in China[J]. Climatic and Environmental Research, 2011, 16(5): 543-550. ] | |
| [9] |
Cai Miao, Zhou Yuquan, Liu Jianzhao, et al. Quantifying the cloud water resource: Methods based on observational diagnosis and cloud model simulation[J]. Journal of Meteorological Research, 2020, 34(6): 1256-1270.
doi: 10.1007/s13351-020-9126-6 |
| [10] |
刘菊菊, 游庆龙, 周毓荃, 等. 基于ERA-Interim的中国云水量时空分布和变化趋势[J]. 高原气象, 2018, 37(6): 1590-1604.
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2018.00059 |
|
[Liu Juju, You Qinglong, Zhou Yuquan, et al. Spatiotemporal distribution and trend of cloud water content in China based on ERA-Interim reanalysis[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2018, 37(6): 1590-1604. ]
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2018.00059 |
|
| [11] | 杨大生, 王普才. 中国地区夏季6—8月云水含量的垂直分布特征[J]. 大气科学, 2012, 36(1): 89-101. |
| [Yang Dasheng, Wang Pucai. Characteristics of vertical distributions of cloud water contents over China during summer[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 2012, 36(1): 89-101. ] | |
| [12] | 刘洪利, 朱文琴, 宜树华, 等. 中国地区云的气候特征分析[J]. 气象学报, 2003, 61(4): 466-473. |
| [Liu Hongli, Zhu Wenqin, Yi Shuhua, et al. Climatic analysis of the cloud over China[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2003, 61(4): 466-473. ] | |
| [13] | 张沛, 姚展予, 贾烁, 等. 六盘山地区空中水资源特征及水凝物降水效率研究[J]. 大气科学, 2020, 44(2): 421-434. |
| [Zhang Pei, Yao Zhanyu, Jia Shuo, et al. Study of the characteristics of atmospheric water resources and hydrometeor precipitation efficiency over the Liupan Shan area[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 2020, 44(2): 421-434. ] | |
| [14] | 石岩, 饶丹. 新疆水资源现状及其可持续利用对策分析[J]. 华北水利水电大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 36(4): 36-38. |
| [Shi Yan, Rao Dan. Analysis on present situation of water resources and sustainable utilization countermeasures of Xinjiang[J]. Journal of North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 36(4): 36-38. ] | |
| [15] | 陈勇航, 邓军英, 张萍, 等. 中天山附近强降水过程中云冰水含量随高度变化特征[J]. 资源科学, 2013, 35(3): 655-664. |
| [Chen Yonghang, Deng Junying, Zhang Ping, et al. Vertical distribution of ice water content in clouds during heavy rains around Tianshan Mountain[J]. Resources Science, 2013, 35(3): 655-664. ] | |
| [16] | 张小娟, 王军, 黄观, 等. 新疆3大山区云中液态水时空分布特征[J]. 干旱区研究, 2018, 35(4): 846-854. |
|
[Zhang Xiaojuan, Wang Jun, Huang Guan, et al. Spatiotemporal distribution of cloud liquid water volume over three main mountains in Xinjiang[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2018, 35(4): 846-854. ]
doi: 10.13866/j.azr.2018.04.12 |
|
| [17] | 白磊, 王维霞, 姚亚楠, 等. ERA-Interim 和NCEP/NCAR 再分析数据气温和气压值在天山山区适用性分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 2013, 7(3): 51-56. |
| [Bai Lei, Wang Weixia, Yao Ya’nan, et al. Reliability of NCEP/NCAR and ERA-Interim reanalysis data on Tianshan Mountainous area[J]. Desert and Oasis Meteorology, 2013, 7(3): 51-56. ] | |
| [18] | 石晓兰, 杨青, 姚俊强, 等. 基于ERA-Interim资料的中国天山山区云水含量空间分布特征[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 2016, 10(2): 50-56. |
| [Shi Xiaolan, Yang Qing, Yao Junqiang, et al. The spatial distribution of water vapor and cloud water content over Tianshan Mountains, China based on ERA-Interim dataset[J]. Desert and Oasis Meteorology, 2016, 10(2): 50-56. ] | |
| [19] | Liu Jin, Liang Hong, Yang Lianmei. Comparative analysis of precipitable water vapor data in the Tarim Basin, China[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2024, 74(7): 2846-2858. |
| [20] | Zeng Yong, Yang Lianmei, Tong Zepeng, et al. Seasonal variation in total cloud cover and cloud type characteristics in Xinjiang, China based on FY-4A[J]. Remote Sensing, 2024, 16(15): 2803. |
| [21] | 郝小红, 宋敏红, 周梓萱. 夏季青藏高原空中云水资源的时空特征分析[J]. 高原气象, 2020, 39(6): 1339-1347. |
|
[Hao Xiaohong, Song Minhong, Zhou Zixuan. Temporal and spatial characteristics of water vapor and cloud water over the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau in summer[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2020, 39(6): 1339-1347. ]
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2019.00135 |
|
| [22] | Sun Bo, Zhu Yali, Wang Huijun. The recent interdecadal and interannual variation of water vapor transport over Eastern China[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2011, 28(5): 1039-1048. |
| [23] |
刘晶, 刘兆旭, 杨莲梅, 等. 塔里木盆地及其周边地区大气可降水量分布及其与降水关系的研究[J]. 高原气象, 2024, 43(3): 617-634.
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2023.00083 |
|
[Liu Jing, Liu Zhaoxu, Yang Lianmei, et al. The characteristics of atmospheric precipitable water vapor distribution and its relationship with precipitation over Tarim Basin and its surrounding area[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2024, 43(3): 617-634. ]
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2023.00083 |
|
| [24] | 王凯, 孙美平, 巩宁刚. 西北地区大气水汽含量时空分布及其输送研究[J]. 干旱区地理, 2018, 41(2): 290-297. |
| [Wang Kai, Sun Meiping, Gong Ninggang. Spatial and temporal distribution and transportation of the water vapor in the northwestern China[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2018, 41(2): 290-297. ] | |
| [25] | Huang Wei, Feng Song, Chen Jianhui, et al. Physical mechanisms of summer precipitation variations in the Tarim Basin in Northwestern China[J]. Journal of Climate, 2015, 28(9): 3579-3591. |
| [26] | Zhao Yong, Huang Anning, Zhou Yang, et al. Impact of the middle and upper tropospheric cooling over Central Asia on the summer rainfall in the Tarim Basin, China[J]. Journal of Climate, 2014, 27(12): 4721-4732. |
| [27] |
李帅, 陈勇航, 侯小刚, 等. FY-2F云量产品在新疆区域的评估及检验[J]. 干旱区研究, 2021, 38(4): 1031-1039.
doi: 10.13866/j.azr.2021.04.14 |
|
[Li Shuai, Chen Yonghang, Hou Xiaogang, et al. Evaluation of FY-2F satellite cloud products in Xinjiang[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2021, 38(4): 1031-1039. ]
doi: 10.13866/j.azr.2021.04.14 |
|
| [28] | 张强, 杨金虎, 王朋岭, 等. 西北地区气候暖湿化的研究进展与展望[J]. 科学通报, 2023, 68(14): 1814-1828. |
| [Zhang Qiang. Yang Jinhu, Wang Pengling, et al. Progress and prospect on climate warming and humidification in Northwest China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2023, 68(14): 1814-1828. ] | |
| [29] |
丁一汇, 柳艳菊, 徐影, 等. 全球气候变化的区域响应: 中国西北地区气候“暖湿化”趋势、成因及预估研究进展与展望[J]. 地球科学进展, 2023, 38(6): 551-562.
doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2023.027 |
|
[Ding Yihui, Liu Yanju, Xu Ying, et al. Regional responses to global climate change: Progress and prospects for trend, causes, and projection of climatic warming-wetting in Northwest China[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2023, 38(6): 551-562. ]
doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2023.027 |
|
| [30] |
张红丽, 韩富强, 张良, 等. 西北地区气候暖湿化空间与季节差异分析[J]. 干旱区研究, 2023, 40(4): 517-531.
doi: 10.13866/j.azr.2023.04.01 |
|
[Zhang Hongli, Han Fuqiang, Zhang Liang, et al. Analysis of spatial and seasonal variations in climate warming and humidification in Northwest China[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2023, 40(4): 517-531. ]
doi: 10.13866/j.azr.2023.04.01 |
|
| [31] |
张强, 杨金虎, 马鹏里, 等. 西北地区气候暖湿化增强东扩特征及其形成机制与重要环境影响[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(3): 351-358.
doi: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-03-0351 |
| [Zhang Qiang, Yang Jinhu, Ma Pengli, et al. The enhancement and eastward expansion of climate warming and humidification, formation mechanism and important environmental impacts in Northwest China[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(3): 351-358. ] | |
| [32] | 王瑞英, 周文韬, 任丹阳, 等. 基于ERA5资料的陕西地区云水资源评估[J]. 陕西气象, 2023(6): 10-16. |
| [Wang Ruiying, Zhou Wentao, Ren Danyang, et al. Assessment of cloud water resources in Shaanxi Province based on ERA5 data[J]. Journal of Shaanxi Meteorology, 2023(6): 10-16. ] | |
| [33] |
张玉欣, 马学谦, 韩辉邦, 等. 2014—2018年青海省云水资源时空分布特征[J]. 干旱区研究, 2021, 38(5): 1254-1262.
doi: 10.13866/j.azr.2021.05.07 |
|
[Zhang Yuxin, Ma Xueqian, Han Huibang, et al. Analysis of spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of cloud water resources in Qinghai Province from 2014 to 2018[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2021, 38(5): 1254-1262. ]
doi: 10.13866/j.azr.2021.05.07 |
|
| [34] |
把黎, 尹宪志, 庞朝云, 等. 祁连山地区夏季南坡与北坡空中云水资源差异性分析[J]. 干旱区研究, 2022, 39(5): 1345-1359.
doi: 10.13866/j.azr.2022.05.02 |
|
[Ba Li, Yin Xianzhi, Pang Zhaoyun, et al. Characteristics of the difference in air water resources between the north and south slopes of the Qilian Mountains in the summer[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2022, 39(5): 1345-1359. ]
doi: 10.13866/j.azr.2022.05.02 |
| [1] | WEN Di, LYU Aifeng, LI Taohui, ZHANG Wenxiang. Characteristics and development potential analysis of agricultural solar-thermal resources in the Tarim Basin [J]. Arid Zone Research, 2025, 42(2): 384-396. |
| [2] | TIAN Wenjun, XUE Yibo, ZHANG Xiaoxiao, LEI Jiaqiang, LI Shengyu, FAN Jinglong, ZHANG Heng. Study on the vertical distribution and transport of dust aerosols during typical dust weather events in the Tarim Basin, Northwest China in spring, 2021 [J]. Arid Zone Research, 2025, 42(1): 14-26. |
| [3] | WANG Ting, SHEN Ganhua, LIU Bing, SUN Yinglin, WANG Zaiguang. Evolution characteristics of spatial and temporal distribution pattern and driving force analysis of reservoirs in the economic zone on the north slope of Tianshan Mountains [J]. Arid Zone Research, 2024, 41(9): 1456-1467. |
| [4] | LONG Weiyi, SHI Jianfei, LI Shuangyuan, SUN Jinjin, WANG Yugang. Evaluation of multimodel inversion effects on soil salinity in oasis basin [J]. Arid Zone Research, 2024, 41(7): 1120-1130. |
| [5] | CHENG Qiulian, LIU Jie, YANG Zhiwei, ZHANG Tianyi, WANG Bin. Spatial distribution and factor analysis of avalanche in the Aerxiangou section of the Duku expressway [J]. Arid Zone Research, 2024, 41(2): 220-229. |
| [6] | ZHU Congzhen,ZHAO Tianliang,MENG Lu,YANG Xinghua,HE Qing,Ali MAMTIMIN. Objective weather classification of persistent floating dust weather in the Tarim Basin [J]. Arid Zone Research, 2023, 40(9): 1391-1403. |
| [7] | ZHAO Meiliang, CAO Guangchao, ZHAO Qinglin, CAO Shengkui. Effects of climate and land use change on the spatial distribution of hydrological factors in the source region of Datong River [J]. Arid Zone Research, 2023, 40(3): 381-391. |
| [8] | CHENG Hongxia, LIN Yuejiang, CHEN Peng, LIANG Fengchao, WANG Yong. Spatial characteristics of sand-dust weather days and influencing factors in the Tarim Basin [J]. Arid Zone Research, 2023, 40(11): 1707-1717. |
| [9] | XU Qiao,ZHAO Wanyu,WEI Yan,YE Mao,ZHAO Xinfeng. Forestry structure and spatial distribution pattern of different age tree species in forest area of eastern Altai Mountain [J]. Arid Zone Research, 2022, 39(6): 1885-1895. |
| [10] | GAO Jie,ZHAO Yong,YAO Junqiang,Dilinuer TUOLIEWUBIEKE,WANG Mengyuan. Spatiotemporal evolution of atmospheric water cycle factors in arid regions of Central Asia under climate change [J]. Arid Zone Research, 2022, 39(5): 1371-1384. |
| [11] | LI Zehou,LI Ruixi,ZHANG Shubin,WANG Chongbin,ZHENG Mingming,DONG Yeqing,WU Xue. Responses of leaf structural and chemical trait of Tamarix ramosissima to soil water changes [J]. Arid Zone Research, 2022, 39(5): 1486-1495. |
| [12] | LUO Chengyan,CHEN Fulong,HE Chaofei,LONG Aihua,QIAO Changlu. Applicability of CMADS in runoff simulation of Yulong Kashi River [J]. Arid Zone Research, 2022, 39(4): 1090-1101. |
| [13] | HU Changtong,YANG Tao,WAN Xuhao,SUN Laikang,ZHENG Yiwen,YAN Xuerong. Distribution characteristics of heavy metals in river sediments and their relationship with land use types in Xi’an City [J]. Arid Zone Research, 2022, 39(4): 1270-1281. |
| [14] | WANG Jiawen,PENG Jie,JI Wenjun,BAI Jianduo,FENG Chunhui,LI Hongyi. Soil pH inversion based on electromagnetic induction data in cotton field of southern Xinjiang [J]. Arid Zone Research, 2022, 39(4): 1293-1302. |
| [15] | SUN Congjian,CHEN Wei,WANG Shiyu. Stream component characteristics of the inland river basin of the Tarim Basin under regional climate change [J]. Arid Zone Research, 2022, 39(1): 113-122. |
|
||