
Arid Zone Research ›› 2022, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (6): 1739-1752.doi: 10.13866/j.azr.2022.06.05
• Weather and Applied Climate • Previous Articles Next Articles
CAO Yiqing1( ),LONG Xiao1(
),LONG Xiao1( ),LI Chao1,WANG Siyi1,ZHAO Jianhua2
),LI Chao1,WANG Siyi1,ZHAO Jianhua2
Received:2022-04-23
Revised:2022-05-23
Online:2022-11-15
Published:2023-01-17
Contact:
Xiao LONG
E-mail:oucyiqing2015@163.com;longxiao@lzu.edu.cn
CAO Yiqing,LONG Xiao,LI Chao,WANG Siyi,ZHAO Jianhua. Numerical study on the effect of low-level jet on two rainstorms on the east side of the Helan Mountain[J].Arid Zone Research, 2022, 39(6): 1739-1752.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
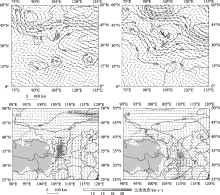
Fig. 2
Composition of geopotential height (contour, unit: dagpm, brown lines denotes tough and shear line, the grey shade is the terrain height) and wind field (vector, unit: m·s-1, the shaded represent the region of wind speed ≥12 m·s-1) on 500 hPa and 700 hPa at 18:00 on 18 July 2018 and 06:00 on 4 June 2017"

Tab. 1
WRF pattern grid design and parameterized scheme configuration"
| 模拟域 | D01 | D02 | D03 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 格距 | 27 km | 9 km | 3 km |
| 格点数 | 181×181 | 181×181 | 181×181 |
| 微物理过程 | WSM6/WSM5 | WSM6/WSM5 | WSM6/WSM5 |
| 长波辐射 | RRTM | RRTM | RRTM |
| 短波辐射 | Goddard | Goddard | Goddard |
| 积云参数化 | Grell-Devenyi | Grell-Devenyi | 无 |
| 陆面过程 | RUC/Noah | RUC/Noah | RUC/Noah |
| 边界层过程 | YSU | YSU | YSU |
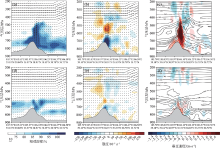
Fig. 10
The vertical profile of the relative humidity (unit: %), divergence field (unit: 10-5 s-1) with wind field (unit: m·s-1) and pseudo-equivalent potential temperature (unit: K) with vertical velocity (unit: m·s-1) of control tests (a, b, c) and reduced jet stream tests (d, e, f), where W*10 at 04:00 on July 19, 2018"

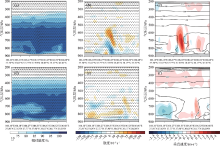
Fig. 11
The vertical profile of the relative humidity (unit: %), divergence field (unit: 10-5 s-1) with wind field (unit: m·s-1) and pseudo-equivalent potential temperature (unit: K) with vertical velocity (unit: m·s-1) of control tests (a, b, c) and reduced jet stream tests (d, e, f), where W*10 at 15:00 on June 4, 2017"

Tab. 2
Water vapor flux budget at each boundary /(kg·m-1·s-1)"
| 个例 | 急流类型 | 试验名称 | 东边界 | 西边界 | 东-西 | 南边界 | 北边界 | 南-北 | 净输入 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| “7·18”过程23:00 | 偏南急流 | CTL1 | 38.77 | 15.64 | 23.13 | 102.66 | 44.99 | 57.67 | 34.54 |
| EXP1 | 31.84 | 12.80 | 19.04 | 58.23 | 34.58 | 23.65 | 4.61 | ||
| “6·04”过程13:00 | 东南急流 | CTL2 | -18.00 | 1.92 | -19.92 | 23.55 | 23.98 | -0.44 | 19.48 |
| EXP2 | -13.22 | 8.08 | -21.30 | 11.99 | 15.19 | -3.20 | 18.10 |
| [1] | 刘鸿波, 何明洋, 王斌, 等. 低空急流的研究进展与展望[J]. 气象学报, 2014, 72(2): 191-206. |
| [ Liu Hongbo, He Mingyang, Wang Bin, et al. Advances in low-level jet research and future prospects[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2014, 72(2): 191-206. ] | |
| [2] |
Stensrud D J. Importance of low-level jets to climate: A review[J]. Journal of Climate, 1996, 9(8): 1698-1711.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(1996)009<1698:IOLLJT>2.0.CO;2 |
| [3] | Goualt J. Vents en altitude a fort Lamy(Tchad)[J]. Annales Physque du Globe de la France d’Outre-Mer, 1938, 5: 70-91. |
| [4] |
Farquharson J S. The diurnal variation of wind over tropical Africa[J]. Quarterly Journal of The Royal Meteorological Society, 1939, 65(280): 165-184.
doi: 10.1002/qj.49706528004 |
| [5] |
Means L L. On thunderstorm forecasting in the central United States[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 1952, 80(10): 165-189.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1952)080<0165:OTFITC>2.0.CO;2 |
| [6] |
Higgins R, Yao Y, Yarosh E, et al. Influence of the Great Plains low-level jet on summertime precipitation and moisture transport over the central United States[J]. Journal of Climate, 1997, 10(3):481-507.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(1997)010<0481:IOTGPL>2.0.CO;2 |
| [7] | 翟国庆, 丁华君, 孙淑清, 等. 与低空急流相伴的暴雨天气诊断研究[J]. 大气科学, 1999, 23(1): 112-118. |
| [ Zhai Guoqing, Ding Huajun, Sun Shuqing, et al. Physical characteristics of heavy rainfall associated with strong low level jet[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 1999, 23(1): 112-118. ] | |
| [8] | 何光碧, 陈静, 李川, 等. 低涡与急流对“04.9”川东暴雨影响的分析与数值模拟[J]. 高原气象, 2005, 24(6): 1012-1023. |
| [ He Guangbi, Chen Jing, Li Chuan, et al. Analysis and numerical simulation for effects of vortex and jet stream on heavy rain in East Sichuan in September 2004[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2005, 24(6): 1012-1023. ] | |
| [9] |
Trier S B, Davis C A, Ahijevych D A, et al. Mechanisms supporting long lived episodes of propagating nocturnal convection within a 7-day WRF model simulation[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 2006, 63(10):2437-2461.
doi: 10.1175/JAS3768.1 |
| [10] |
Tuttle J D, Davis C A. Corridors of warm season precipitation in the Central United States[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 2006, 134(9): 2297-2317.
doi: 10.1175/MWR3188.1 |
| [11] |
Du Yu, Chen Guixing. Climatology of low-level jets and their impact on rainfall over southern China during the early summer rainy season[J]. Journal of Climate, 2019b, 32(24): 8813-8833.
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-19-0306.1 |
| [12] | 梁红丽, 程正泉. 2014年两次相似路径影响云南台风降水差异成因分析[J]. 气象, 2017, 43(11): 1339-1353. |
| [ Liang Hongli, Cheng Zhengquan. Cause analysis of precipitation difference between two typhoons influencing Yunnan along similar tracks in 2014[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2017, 43(11): 1339-1353. ] | |
| [13] | 郑婧, 许爱华, 孙素琴, 等. 高空西北气流下特大暴雨的预报误差分析及思考[J]. 气象, 2018, 44(1): 93-106. |
| [ Zhen Jin, Xu Aihua, Sun Suqin, et al. Forecast error analysis of extremely heavy rain under high-level northwest flow[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2018, 44(1): 93-106. ] | |
| [14] | 陈健康, 赵玉春, 陈赛, 等. 闽中南罕见冬季锋前暴雨个例特征分析[J]. 气象, 2019, 45(2): 228-239. |
| [ Chen Jiankang, Zhao Yuchun, Chen Sai, et al. Characteristic analysis on a winter prefrontal torrential rain in central and southern Fujian[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2019, 45(2): 228-239. ] | |
| [15] | 顾清源, 肖递祥, 黄楚惠, 等. 低空急流在副高西北侧连续性暴雨中的触发作用[J]. 气象, 2009, 35(4): 59-67. |
| [ Gu Qingyuan, Xiao Dixiang, Huang Chuhui, et al. Trigger role of the low-level jet for the continuous rainstorm in the northwest side of subtropical high[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2009, 35(4): 59-67. ] | |
| [16] |
Zhao Yuchun. Numerical investigation of a localized extremely heavy rainfall event in complex topographic area during midsummer[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2012, 113(5): 22-39.
doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2012.04.018 |
| [17] |
许朝斋, 林之光, 汪奕琮. 贺兰山区气候若干问题[J]. 地理学报, 1993, 48(2): 171-176.
doi: 10.11821/xb199302009 |
|
[ Xu Chaozhai, Lin Zhiguang, Wang Yizong. Some problems of Helan Mountain climate[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1993, 48(2): 171-176. ]
doi: 10.11821/xb199302009 |
|
| [18] | 陈豫英, 陈楠, 任小芳, 等. 贺兰山东麓罕见特大暴雨的预报偏差和可预报性分析[J]. 气象, 2018, 44(1): 159-169. |
| [ Chen Yuying, Chen Nan, Ren Xiaofang, et al. Analysis on forecast deviation and predictability of a rare severe rainstorm along the eastern Helan Mountain[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2018, 44(1): 159-169. ] | |
| [19] | Chen Yuying, Li Jianping, Li Xin, et al. Spatio-temporal distribution of the rainstorm in the east side of the Helan Mountain and the possible causes of its variability[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2021, 252: 105469. 1-105469.16. |
| [20] | 陈晓娟, 王咏青, 毛璐, 等. 贺兰山区两次极端暴雨动力作用数值模拟分析[J]. 干旱区研究, 2020, 37(3): 680-688. |
| [ Chen Xiaojuan, Wang Yongqin, Mao Lu, et al. Numerical simulation analysis of the dynamic effects of terrain on two extreme rainstorms on Helan Mountain[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2020, 37(3): 680-688. ] | |
| [21] |
王晖, 隆霄, 温晓培, 等. 2012年宁夏“7·29”大暴雨过程的数值模拟研究[J]. 高原气象, 2017, 36(1): 268-281.
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2016.00017 |
|
[ Wang Hui, Long Xiao, Wen Xiaopei, et al. Numerical simulation studies on “2012·7·29” rainstorm process in Ningxia[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2017, 36(1): 268-281. ]
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2016.00017 |
|
| [22] |
杨晓军, 叶培龙, 徐丽丽, 等. 一次青藏高原东北侧边坡强对流暴雨的中尺度对流系统演变特征[J]. 高原气象, 2022, 41(4): 839-849.
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2021.00023 |
|
[ Yang Xiaojun, Ye Peilong, Xu Lili, et al. The variation characteristics of mesoscale convection system in a severe convective torrential rain over the northeast slope of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2022, 41(4): 839-849. ]
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2021.00023 |
|
| [23] |
陈豫英, 苏洋, 杨银, 等. 贺兰山东麓极端暴雨的中尺度特征[J]. 高原气象, 2021, 40(1): 47-60.
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2020.00012 |
|
[ Chen Yuying, Su Yang, Yang Yin, et al. The mesoscale characteristics of extreme rainstorm in the eastern region of Helan Mountain[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2021, 40(1): 47-60. ]
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2020.00012 |
|
| [24] | 王智, 高坤, 翟国庆. 一次与西南低涡相联系的低空急流的数值研究[J]. 大气科学, 2003, 27(1): 75-85. |
| [ Wang Zhi, Gao Kun, Zhai Guoqin. A mesoscale numerical simulation of low level jet related with the southwest vortex[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 2003, 27(1): 75-85. ] |
|
||