
Arid Zone Research ›› 2024, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (8): 1272-1287.doi: 10.13866/j.azr.2024.08.02
• Weather and Climate • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Chao1,2( ), LONG Xiao1(
), LONG Xiao1( ), CAO Yiqing1, HAN Zifei3, WANG Hao1, ZHENG Jingyuan1
), CAO Yiqing1, HAN Zifei3, WANG Hao1, ZHENG Jingyuan1
Received:2024-01-19
Revised:2024-04-16
Online:2024-08-15
Published:2024-08-22
Contact:
LONG Xiao
E-mail:lichao_meso@qq.com;longxiao@lzu.edu.cn
LI Chao, LONG Xiao, CAO Yiqing, HAN Zifei, WANG Hao, ZHENG Jingyuan. Ideal numerical tests of topographic precipitation around the Helan Mountain under different wind field structures[J].Arid Zone Research, 2024, 41(8): 1272-1287.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Tab. 1
Precipitation process information"
| 暴雨时段(北京时) | 持续时间/h | 最大雨量/mm |
|---|---|---|
| 2009年7月7日8:00—8日7:00 | 24 | 汝箕沟107.6 |
| 2012年7月29日20:00—30日11:00 | 16 | 滚钟口174.3 |
| 2015年9月3日4:00—4日1:00 | 21 | 小口子65.9 |
| 2015年9月8日1:00—8日20:00 | 20 | 八顷村69.6 |
| 2016年7月24日5:00—12:00 | 8 | 灵武煤矿89.5 |
| 2016年8月13日15:00—14日14:00 | 24 | 王老滩110.2 |
| 2016年8月21日19:00—22日8:00 | 14 | 滑雪场241.7 |
| 2016年8月22日22:00—23日6:00 | 9 | 路家营子村57 |
| 2017年6月4日15:00—5日10:00 | 20 | 黄旗口沟116.5 |
| 2017年7月25日20:00—26日2:00 | 6 | 窑子圈64.4 |
| 2017年7月5日3:00—18:00 | 16 | 滑雪场114.4 |
| 2018年7月19日3:00—10:00 | 8 | 明长城136.2 |
| 2018年7月1日9:00—2日1:00 | 17 | 牛首山84.3 |
| 2018年7月22日19:00—23日7:00 | 13 | 滑雪场277.6 |
| 2018年7月23日12:00—20:00 | 9 | 红翔新村89.3 |
| 2018年8月31日19:00—9月1日17:00 | 23 | 苦水沟136.9 |
| 2018年8月6日12:00—7日16:00 | 29 | 马莲口119.1 |
| 2018年8月9日12:00—10日13:00 | 26 | 临河镇71.4 |
| 2019年8月2日18:00—3日0:00 | 7 | 暖泉农场71 |
| 2020年8月11日7:00—12日8:00 | 26 | 五渠村142.5 |

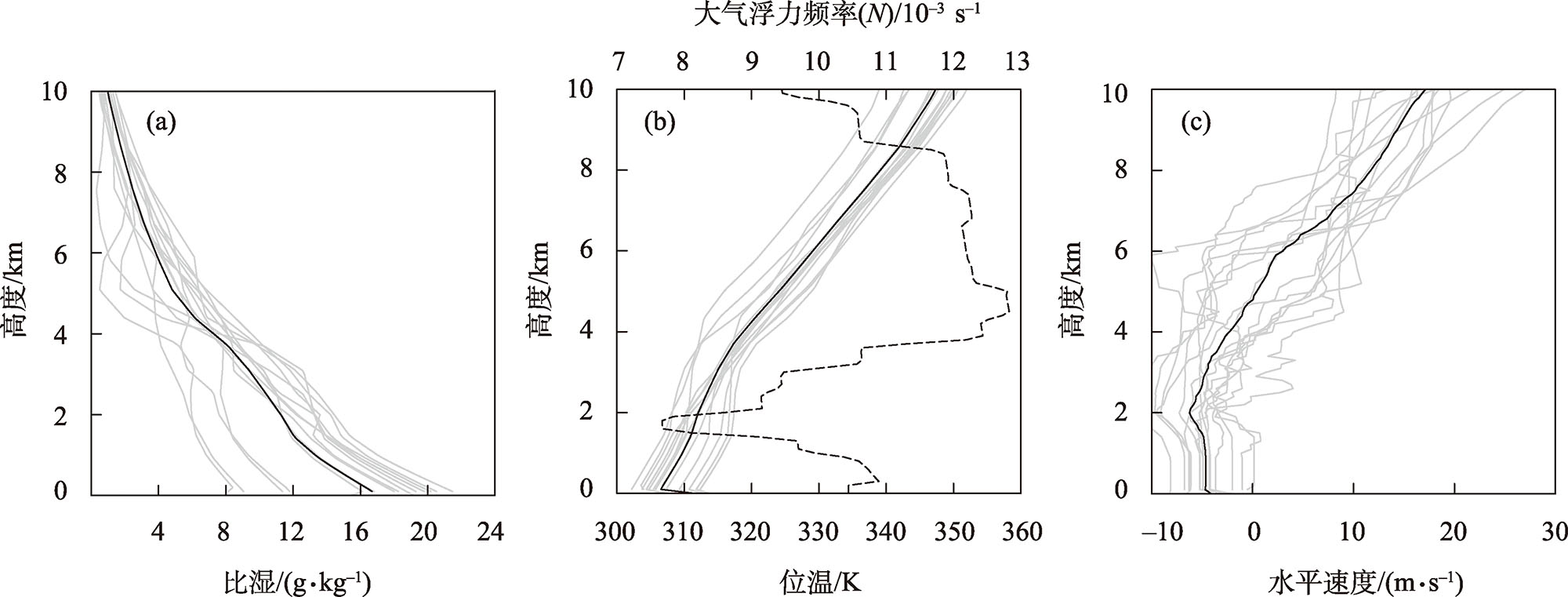
Fig. 2
Vertical distribution (gray solid line) of specific humidity (a, unit: g·kg-1), potential temperature (b, unit: K), wind speed (c, unit: m·s-1) and average distribution of meteorological elements (black solid line) during individual precipitation of 20 rainstorms at the eastern foot of Helan Mountain"
Tab. 2
Design of experiments"
| 试验名称 | N/s-1 | 比湿/(g·g-1) | 风场结构 | 东风/(m·s-1) | 西风/(m·s-1) | 试验目的 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干过程 (WRF-dry) | D1 | N = 0.007 | 0 | (Ⅰ) | u0:-4、-6、-8、-10、-13、-15 | - | 重力波特征 |
| D2 | (Ⅱ) | ushear:-8、-10、-12、-15 | - | ||||
| 湿过程 (WRF-moist) | M1 | 以20次降水过程的平均位温阔线 作为初始场 | 以20次降水过程 的平均比湿阔线 作为初始场 | (Ⅰ) | u0:-4、-5、-6、-7、-8、-9、-10、-11、 -12、-13、-14 | - | 重力波特征、 降水分布 特征 |
| M2 | (Ⅱ) | ushear:-8、-9、-10、-11、-12、-13、-14、 -15、-16、-17、-18、-19、-20、-22 | - | ||||
| M3 | (Ⅲ) | u1:-14 | u2:5、10、20、 30、40 |
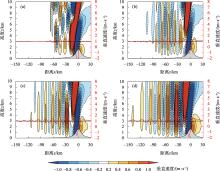
Fig. 5
Vertical velocity field (shadow, unit: m·s-1) and vertical velocity variation at 2 km height on both sides of the mountain (red line, unit: m·s-1) simulated by easterly cross-mountain experiments (D2) with different sizes of wind shear (a: ushear =-8 m·s-1, b: ushear =-10 m·s-1, c: ushear =-12 m·s-1, d: ushear =-15 m·s-1)"

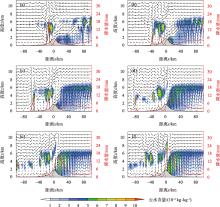
Fig. 9
Simulated cloud water content (shadow, unit: 10-4 kg·kg-1), flow field (vector arrow, unit: m·s-1) vertical profile at 540 min and accumulated precipitation during 480-600 min (red curve, unit: mm) in M1 experiments (a: u0= -6 m·s-1, b: u0= -7 m·s-1, c: u0= -8 m·s-1, d: u0= -9 m·s-1, e: u0= -10 m·s-1, f: u0= -11 m·s-1)"

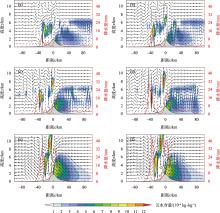
Fig. 12
Simulated cloud water content (shadow, unit: 10-4 kg·kg-1), flow field (vector arrow, unit: m·s-1) vertical profile at 540 min and accumulated precipitation during 480-600 min (red curve, unit: mm) in M2 experiments (a: ushear=-9 m·s-1, b: ushear=-11 m·s-1, c: ushear= -13 m·s-1, d: ushear= -15 m·s-1, e: ushear= -17 m·s-1, f: ushear= -19 m·s-1 )"
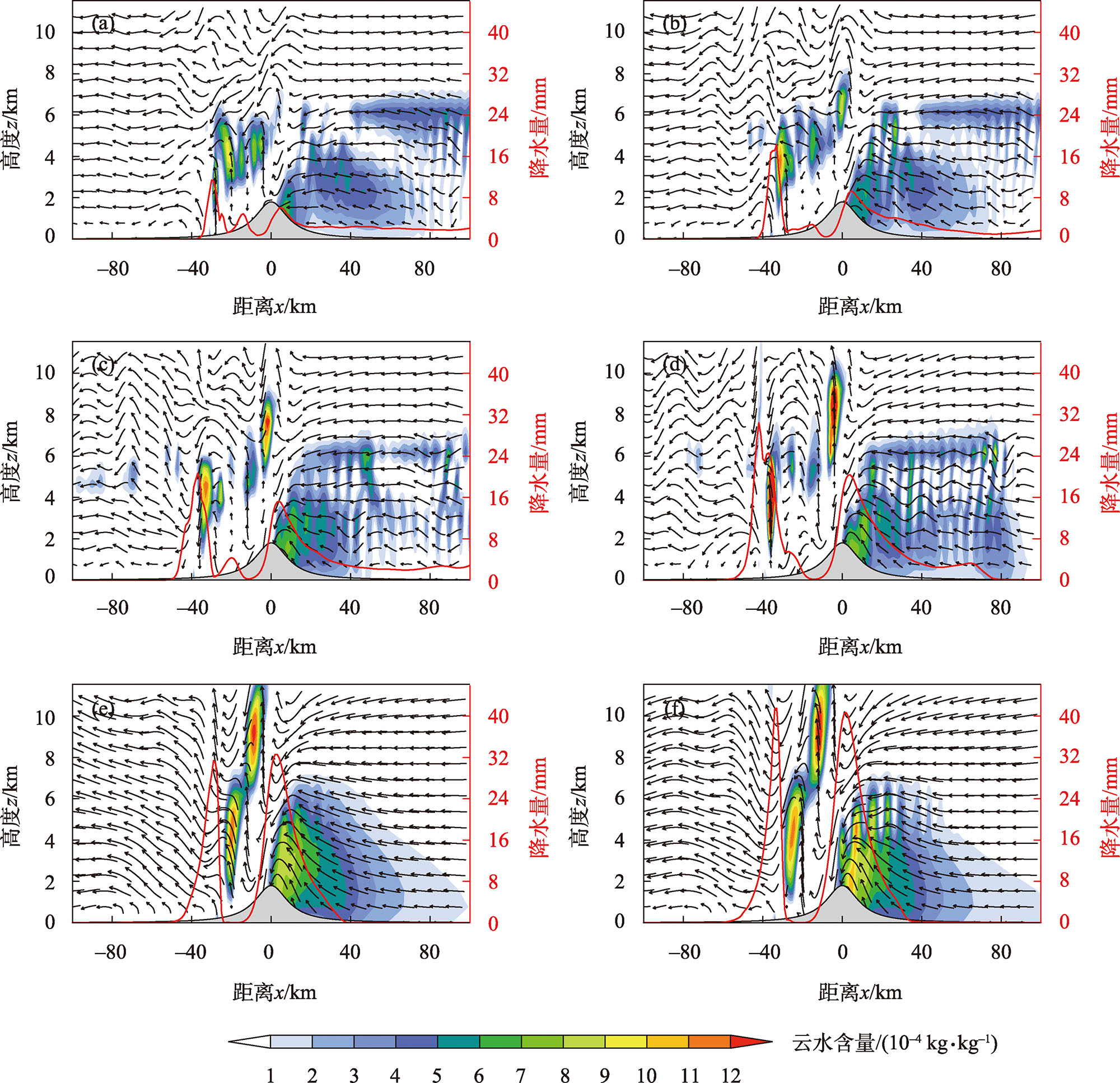
Fig. 14
Simulated cloud water content (shadow, unit: 10-4 kg·kg-1), flow field (vector arrow, unit: m·s-1) vertical profile at 540 min and accumulated precipitation during 480-600 min (red curve, unit: mm) in M3 experiments (u1= -14 m·s-1; u2= 5 m·s-1(b), 10 m·s-1(c), 20 m·s-1(d), 30 m·s-1(e), 40 m·s-1(f) )"

| [1] | Medina S, Houze R A. Air motions and precipitation growth in Alpine storms[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 2003, 129: 345-371. |
| [2] | Rotunno R, Ferretti R. Orographic effects on rainfall in MAP cases IOP 2b and IOP 8[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 2003, 129: 373-390. |
| [3] | Houze, Medina S. Turbulence as a mechanism for orographic precipitation enhancement[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 2005, 62: 3599-3623. |
| [4] | Picard L, Mass C. The sensitivity of orographic precipitation to flow direction: An idealized modeling approach[J]. Journal of Hydro meteorology, 2017, 18(6): 1673-1688. |
| [5] | Morales A, Posselt D J, Morrison H. Which combinations of environmental conditions and microphysical parameter values produce a given orographic precipitation distribution?[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 2021, 78(2): 619-638. |
| [6] | 黄玉霞, 王宝鉴, 黄武斌, 等. 我国西北暴雨的研究进展[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2019, 38(5): 515-525. |
| [ Huang Yuxia, Wang Baojian, Huang Wubin, et al. A review on rainstorm research in northwest China[J]. Torrential Rain and Disasters, 2019, 38(5): 515-525. ] | |
| [7] |
钟水新. 地形对降水的影响机理及预报方法研究进展[J]. 高原气象, 2020, 39(5): 1122-1132.
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2019.00083 |
|
[ Zhong Shuixin. Advances in the study of the influence mechanism and forecast methods for orographic precipitation[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2020, 39(5): 1122-1132. ]
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2019.00083 |
|
| [8] | 李子良. 地形降水试验和背风回流降水机制[J]. 气象, 2006, 32(5): 10-15. |
| [ Li Ziliang. Simulations of precipitation induced by reversal flow in lee of mountain[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2006, 32(5): 10-15. ] | |
| [9] | Scorer R S. Theory of waves in lee of mountains[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 1949, 75: 41-56. |
| [10] | Lin Yuh-Lang, Wang T A. Flow regimes and transient dynamics of two-dimensional stratified flow over an isolated mountain ridge[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 1996, 53(1): 139-158. |
| [11] | 李子良. 三维多层流动过孤立山脉产生的山脉重力波的数值试验[J]. 北京大学学报: 自然科学版, 2006, 42(3): 351-356. |
| [ Li Ziliang. Numerical simulations of mountain gravity waves generated by multi-layer flow over an isolated mountain[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2006, 42(3): 351-356. ] | |
| [12] | Xue H, Giorgetta M A. A large-eddy simulation study on the diurnally evolving nonlinear trapped lee waves over a two-dimensional steep mountain[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 2021, 78(2): 399-415. |
| [13] | Colle, Brian A. Sensitivity of orographic precipitation to changing ambient conditions and terrain geometries: An idealized modeling perspective[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 2004, 61(5): 588-606. |
| [14] | 杨婷, 闵锦忠, 张申龑. 分层气流条件下地形降水的二维理想数值试验[J]. 气象科学, 2017, 37(2): 222-230. |
| [ Yang Ting, Min Jinzhong, Zhang Shenyan. Two-dimensional idealized numerical experiments on the orographic rainfall with a stratified flow over mountain[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Sciences, 2017, 37(2): 222-230. ] | |
| [15] | 郭欣, 郭学良, 付丹红, 等. 钟形地形动力抬升和重力波传播与地形云和降水形成关系研究[J]. 大气科学, 2013, 37(4): 786-800. |
| [ Guo Xin, Guo Xueliang, Fu Danhong, et al. Relationship between bell-shaped terrain dynamic forcing, mountain wave propagation, and orographic clouds and precipitation[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 2013, 37(4): 786-800. ] | |
| [16] | Galewsky J, Sobel A. Moist dynamics and orographic precipitation in northern and Central California during the new year’s flood of 1997[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 2005, 133(6): 1594-1612. |
| [17] | Lorente-Plazas R, Mitchell T P, Mauger G, et al. Local enhancement of extreme precipitation during atmospheric rivers as simulated in a regional climate model[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 2018, 19(9): 1429-1446. |
| [18] | Kirshbaum D J, Smith R B. Temperature and moist-stability effects on midlatitude orographic precipitation[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 2008, 634: 134. |
| [19] | Rotunno R, Houze R A. Lessons on orographic precipitation from the mesoscale alpine programme[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 2007, 133: 811-830. |
| [20] | Mott R, Scipión D, Schneebeli M, et al. Orographic effects on snow deposition patterns in mountainous terrain[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres, 2014, 119: 1419-1439. |
| [21] | 陶林科, 杨侃, 胡文东, 等. “7·30”大暴雨的数值模拟及贺兰山地形影响分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 2014, 8(4): 32-39. |
| [ Tao Linke, Yang Kan, Hu Wendong, et al. The contribution of Helan mountain to the formation of a heavy rainstorm occurred over Yinchuan Plain by numerical simulation[J]. Desert and Oasis Meteorology, 2014, 8(4): 32-39. ] | |
| [22] |
王晖, 隆霄, 温晓培, 等. 2012年宁夏“7·29”大暴雨过程的数值模拟研究[J]. 高原气象, 2017, 36(1): 268-281.
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2016.00017 |
| [ Wang Hui, Long Xiao, Wen Xiaopei, et al. Numerical simulation studies on “2012∙7∙29” rainstorm process in Ningxia[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2017, 36(1): 268-281.] | |
| [23] | 陈晓娟, 王咏青, 毛璐, 等. 贺兰山区两次极端暴雨动力作用数值模拟分析[J]. 干旱区研究, 2020, 37(3): 680-688. |
| [ Chen Xiaojuan, Wang Yongqing, Mao Lu, et al. Numerical simulation analysis of the dynamic effects of terrain on two extreme rainstorms on Helan Mountain[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2020, 37(3): 680-688. ] | |
| [24] |
陈豫英, 苏洋, 杨银, 等. 贺兰山东麓极端暴雨的中尺度特征[J]. 高原气象, 2021, 40(1): 47-60.
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2020.00012 |
|
[ Chen Yuying, Su Yang, Yang Yin, et al. The mesoscale characteristics of extreme rainstorm in the eastern region of Helan Mountain[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2021, 40(1): 47-60. ]
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2020.00012 |
|
| [25] | Sever G, Lin Y L. Dynamical and physical processes associated with orographic precipitation in a conditionally unstable uniform flow: Variation in basic wind speed[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric sciences, 2016, 74(2): 449-466. |
| [26] |
刘晶, 李娜, 陈春艳. 新疆北部一次暖区暴雪过程锋面结构及中尺度云团分析[J]. 高原气象, 2018, 37(1): 158-166.
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2017.00008 |
|
[ Liu Jing, Li Na, Chen Chunyan. The frontal structure and analysis on mesoscale cloud characteristic during a warm zone blizzard process in north Xinjiang[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2018, 37(1): 158-166. ]
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2017.00008 |
|
| [27] |
赵庆云, 张武, 陈晓燕, 等. 一次六盘山两侧强对流暴雨中尺度对流系统的传播特征[J]. 高原气象, 2018, 37(3): 767-776.
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2017.00068 |
|
[ Zhao Qingyun, Zhang Wu, Chen Xiaoyan, et al. Propagation characteristics of mesoscale convection system in a event of severe convection rainstorm over both sides of Liupanshan Mountains[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2018, 37(3): 767-776. ]
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2017.00068 |
|
| [28] | 姜志斌. 贺兰山地区气候变化和极端天气特征分析[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2016. |
| [ Jiang Zhibin. Analysis of Regional Climate Change and Extreme Weather Characteristics in Helan Mountains Region[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2016. ] | |
| [29] | Chen Yuying, Li Jianping, Li Xin, et al. Spatio-temporal distribution of the rainstorm in the east side of the Helan Mountain and the possible causes of its variability[J]. Atmospheric Research, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2021.105469. |
| [30] | Skamarock W C, Klemp J B, Dudhia J, et al. A description of the advanced research WRF version 3[J]. NCAR Technical Note NCAR/TN-475+STR. June 2008. Mesoscale and Microscale Meteorology Division. National Center for Atmospheric Research, 2008, 475. |
| [31] | 李驰钦, 左群杰, 高守亭, 等. 青藏高原上空一次重力波过程的识别与天气影响分析[J]. 气象学报, 2018, 76(6): 904-919. |
| [ Li Chiqin, Zuo Qunjie, Gao Shouting, et al. Identification of a gravity wave process over the Tibetan Plateau and its impact on the weather[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2018, 76(6): 904-919. ] | |
| [32] | Smolarkiewicz P K, Rotunno R. Low Froude number flow past three-dimensional obstacles. Part I: Baroclinically generated lee vortices[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 1989, 46: 1154-1164. |
| [33] | Smolarkiewicz P K, Rotunno R. Low Froude number flow past three dimensional obstacles. Part II: Upwind flow reversal zone[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 1990, 47: 1498-1511. |
| [34] | 《西北暴雨》编写组. 西北暴雨[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 1992. |
| [ Editorial Group of “Northwest Rainstorm”. Northwest Rainstorm[M]. Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 1992. ] | |
| [35] | 朱乾根, 林锦瑞, 寿邵文, 等. 天气学原理和方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2007: 320-400. |
| [ Zhu Qiangen, Lin Jinrui, Shou Shaowen, et al. Synoptic Principles and Methods[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2007: 320-400.] | |
| [36] | 李超, 隆霄, 曹怡清, 等. 贺兰山东麓20次暴雨过程环流形势及低空急流特征[J]. 干旱区研究, 2022, 39(6): 1753-1767. |
| [ Li Chao, Long Xiao, Cao Yiqing, et al. Circulation pattern and LLJ characteristics of 20 rainstorm events in the eastern region of the Helan Mountain[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2022, 39(6): 1753-1767. ] | |
| [37] | 苏洋, 陈豫英, 杨侃, 等. 低空急流与贺兰山东麓暴雨过程的相关性研究[J]. 气象, 2023, 49(10): 1171-1186. |
| [ Su Yang, Chen Yuying, Yang Kan, et al. Correlations between low-level jet and rainstorm process in the eastern foot of Helan Mountains[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2023, 49(10): 1171-1186. ] | |
| [38] | 曹怡清, 隆霄, 李超, 等. 低空急流对贺兰山东麓两次暴雨影响的数值模拟研究[J]. 干旱区研究, 2022, 39(6): 1739-1752. |
| [ Cao Yiqing, Long Xiao, Li Chao, et al. Numerical study on the effect of low-level jet on two rainstorms on the east side of the Helan Mountain[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2022, 39(6): 1739-1752. ] |
| [1] | LI Chao,LONG Xiao,CAO Yiqing,WANG Siyi,HAN Zifei,WANG Hui. Circulation pattern and LLJ characteristics of 20 rainstorm events in the eastern region of the Helan Mountain [J]. Arid Zone Research, 2022, 39(6): 1753-1767. |
| [2] | CAO Yiqing,LONG Xiao,LI Chao,WANG Siyi,ZHAO Jianhua. Numerical study on the effect of low-level jet on two rainstorms on the east side of the Helan Mountain [J]. Arid Zone Research, 2022, 39(6): 1739-1752. |
| [3] | QIN Yan, NIU De-Cao, KANG Jian, CAO Ge-Tu, ZHANG Si-Lian, FU Hua. Characteristics of Soil Enzyme Activities in Different Grasslands in the Western Slope of the Helan Mountain, China [J]. , 2012, 29(5): 870-877. |
|
||